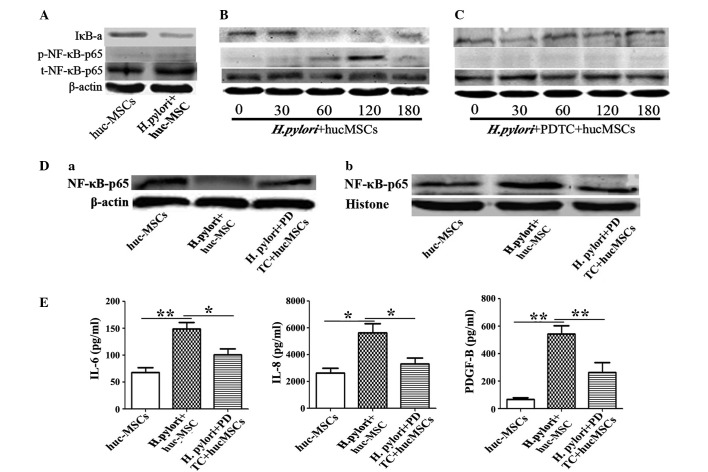
Figure 3.
hucMSCs infected with H. pylori enhance SCG-7901 gastric cancer cell migration via NF-κB activation. (A) H. pylori-induced NF-κB-p65 phosphorylation and IκB-a change in hucMSCs for 24 h. (B and C) Time-course (0, 30, 60, 120, 180 min) of H. pylori induced NF-κB-p65 phosphorylation and IκB-a change in hucMSCs treated with H. pylori in the presence or absence of PDTC (100nM). (D) Western blot analysis of (a) cytoplasmic protein and (b) nucleoprotein expression levels. (E) hucMSCs were pre-incubated with PDTC for 90 min, stimulated with H. pylori for 24 h and then the concentration of cytokines in the cultured medium was determined by ELISA. The NF-κB inhibitor PDTC was able to inhibit the expression of numerous cytokines (IL-6, IL-8 and PDGF-B) in the hucMSCs infected with H. pylori. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation; *P<0.05, **P<0.01; data are representative of three independent experiments. H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori; hucMSCs, human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, PDTC, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; IL, interleukin; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; IκB-a, nuclear factor-κB polypeptide gene enhancer; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; p-NF-κB, phosphorylated NF-κB; t-NF-κB, total NF-κB.