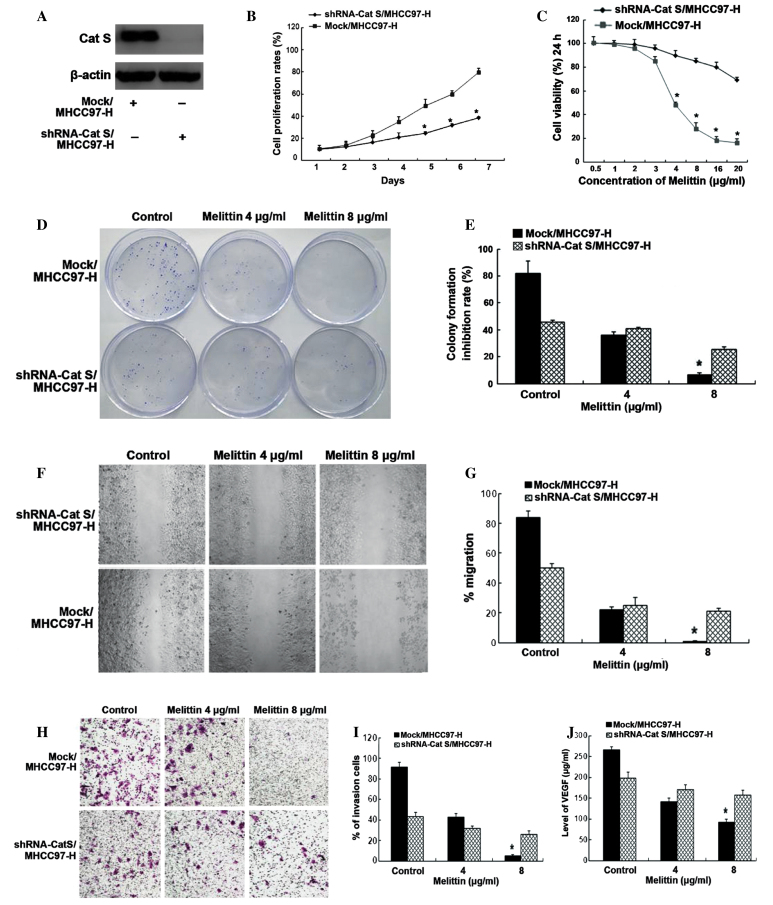
Figure 2.
Melittin prevents stably transfected MHCC97-H cell growth, invasion and angiogenesis. (A) Expression of Cat S was analyzed by western blotting. Levels of β-actin protein were used to monitor for equal loading. (B) Growth curves of stably transfected MHCC97-H cells assessed by MTT assay. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with DMSO treated Mock/MHCC97-H cells). (C) Inhibitory effect of melittin on stably transfected MHCC97-H cells detected by XTT assay. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of ≥3 measurements (*P<0.05 compared with DMSO treated Mock/MHCC97-H cell). (D) Effect of melittin on colony formation of stably transfected MHCC97-H cells. (E) Quantification of colony formation assay. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with DMSO treated Mock/MHCC97-H cell). (F) Effect of melittin on migration of stably transfected MHCC97-H cells was evaluated by wound-healing assay. (G) Quantification of wound-healing assay. Magnification, ×100. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments. (H) Effect of melittin on invasion of stably transfected MHCC97-H cells was evaluated by Transwell chamber assay. Magnification, ×100. (I) Cell number counts of Transwell chamber assay. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with DMSO treated Mock/MHCC97-H cell). (J) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for melittin inhibition of Cat S-associated angiogenesis. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation of 3 independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with shRNA-Cat S/MHCC97-H cells). Cat S, cathepsin S; shRNA, small hairpin RNA.