Fig. 1.
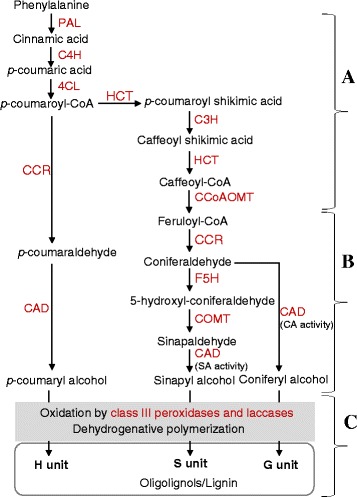
Lignin biosynthesis pathway in plants. The monolignols (coniferyl alcohol, sinapyl alcohol, and p-coumaryl alcohol) synthesized from phenylalanine through the general phenylpropanoid pathway (A) and monolignol-specific pathway (B) are oxidized and incorporated into the G (guaiacyl), S (syringyl) and H (hydroxyphenyl) units, respectively, in the complex and three-dimensional polymer of lignin (C). Oligolignols, which are formed during lignin polymerization, are racemic radical coupling products of monolignols. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; C3H, p-coumarate 3-hydroxylase; HCT, p-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:quinate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase; CCR, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase; F5H, ferulate 5-hydroxylase; COMT, caffeic acid O-methyltransferase; CAD, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase
