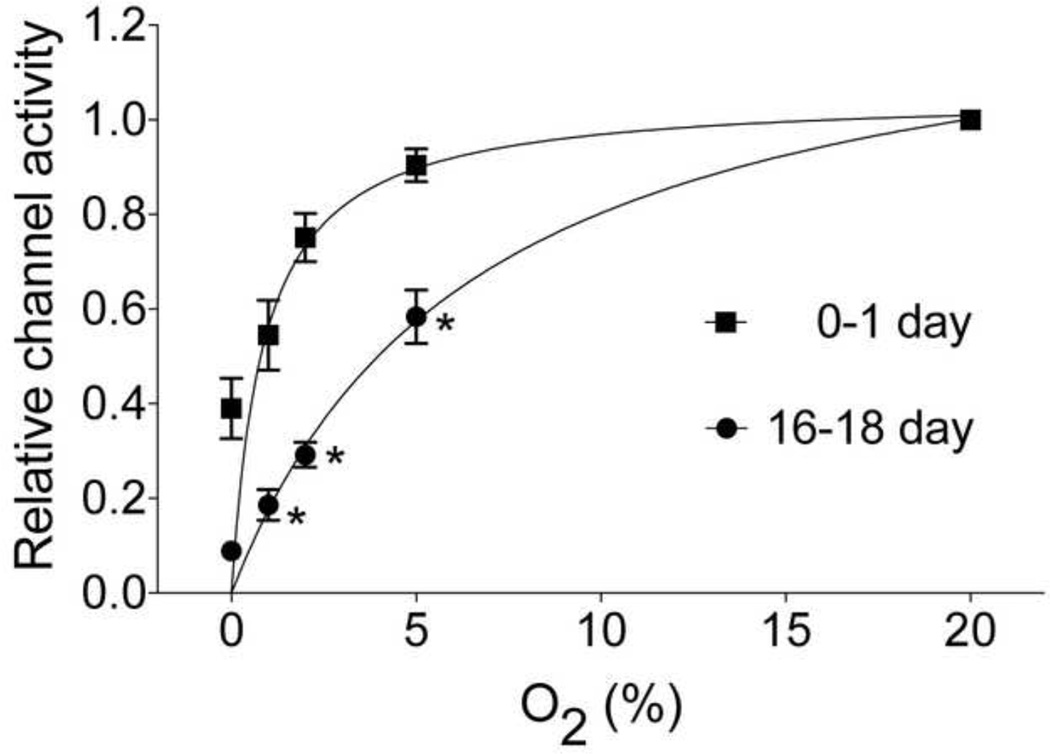
Figure 3.
Age-dependent changes in hypoxia-induced inhibition of TASK in rat glomus cells. Cell-attached patches were formed and pipette potential set at 0 mV. Pipette solution contained (mM) 140 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 5 EGTA, 10 glucose and 10 HEPES (pH 7.3) and the bath perfusion solution contained (mM) 117 NaCl, 23 NaHCO3, 5 KCl, 1 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, and 10 glucose (pH 7.3). Cells were perfused with normoxic and hypoxic solutions. The O2 levels at which half maximal inhibition of TASK was observed was 1.6% O2 for 0–1 day old and 5.3% O2 for 16–18-day old rats. The data points (for TASK activity) were fitted to an exponential function (Y = Yo +(plateau-Yo)(1−exp(−kx)), where x=O2 level, Yo is the Y value when x = zero, plateau is the Y value at maximum x and k is the rate constant). (Reproduced from Kim et al., Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011