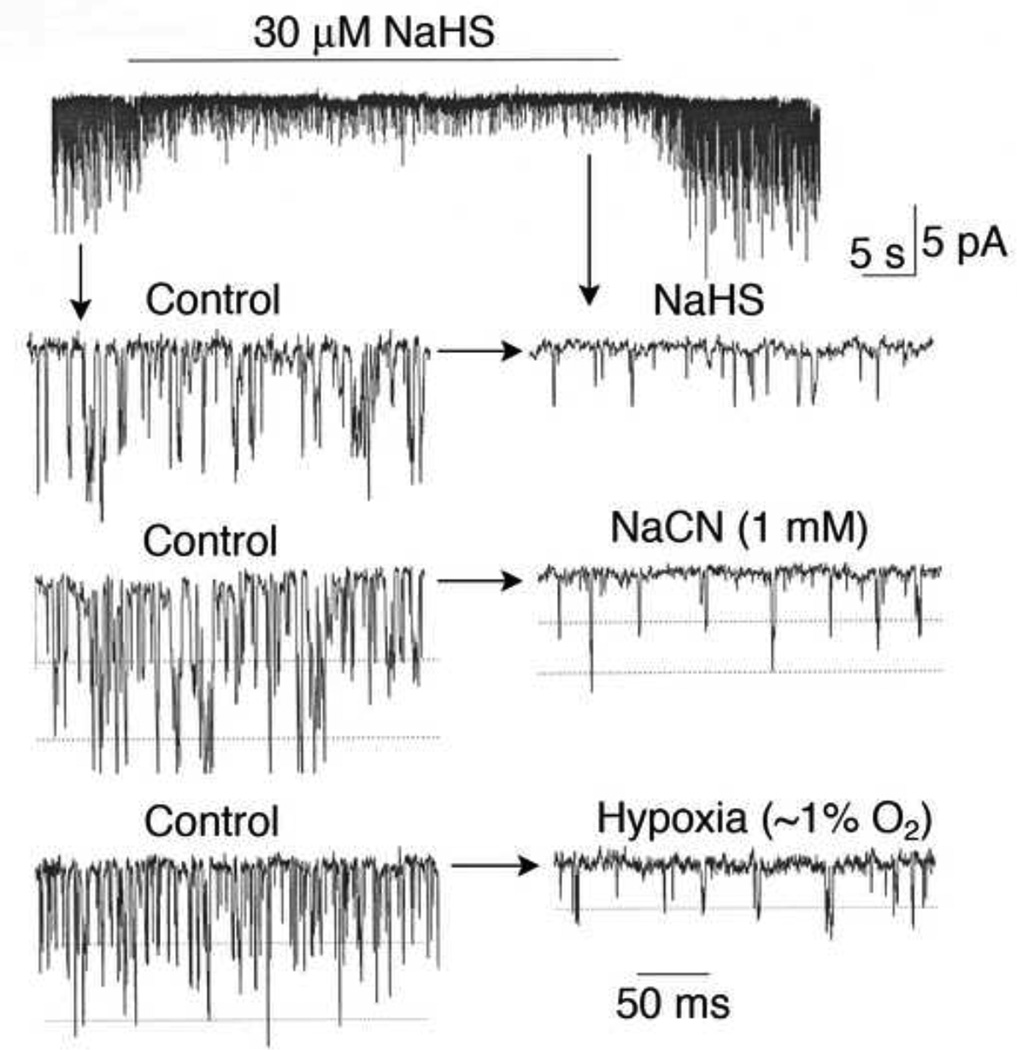
Figure 4.
Inhibition of TASK by hypoxia, sodium cyanide and hydrogen sulfide. Cell-attached patches were formed and pipette potential set at 0 mV. Pipette solution contained (mM) 140 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 5 EGTA, 10 glucose and 10 HEPES (pH 7.3) and the bath perfusion solution contained (mM) 117 NaCl, 23 NaHCO3, 5 KCl, 1 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, and 10 glucose (pH 7.3). Patches containing TASK were perfused with normoxic solution for ~2 min and then perfused for ~1–2 min with solution containing 30 µM NaHS, 1 mM NaCN or with solution bubbled with 0%O2/5%CO2. All three treatments produced ~80% inhibition of TASK activity, and this was associated with the reduction of single channel amplitude produced by cell depolarization from ~−60 mV to ~− 30 mV.