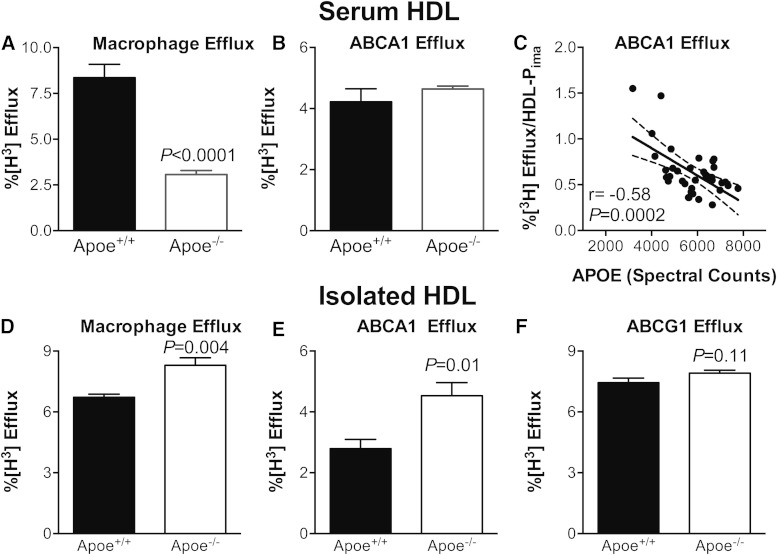
Fig. 6.
Macrophage and ABCA1-specific cholesterol efflux capacity of serum HDL (upper panels) and isolated HDL (lower panels). Macrophage cholesterol efflux capacity (A) and ABCA1-specific cholesterol efflux capacity (B) of serum HDL from wild-type and Apoe−/− mice were measured as described in the legend to Fig. 3. C: Efflux capacity versus the APOE content of HDL isolated by ultracentrifugation from plasma. ABCA1-specific efflux capacity of HDL isolated from the different strains of mice is normalized to HDL particle concentration (HDL-Pima). D–F: Macrophage cholesterol efflux capacity, ABCA1-specific cholesterol efflux capacity, and ABCG1-specific cholesterol efflux capacity of HDL isolated by ultracentrifugation from the plasma of Apoe+/+ and Apoe−/− mice. Cells were incubated with 30 μg HDL protein per milliliter.