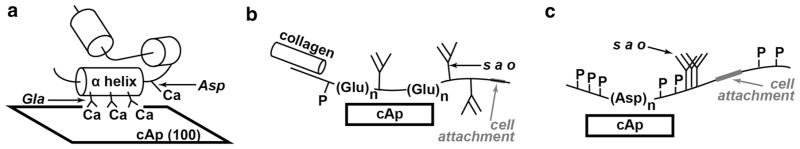
Fig. 5.
Schematic of protein interactions with cAp. The proteins’ carbon backbones are the wavy structures adjacent to the cAp, helical structures are indicated by the labeled cylinders, and phosphorous is indicated by P. a Osteocalcin (OC, i.e., bone Gla protein BGP) binds to the cAp (100) face through three neighboring γ-carboxy glutamic acid (Gla) residues on the same face of the alpha helix. b The acidic glycoprotein bone sialoprotein (BSP) possesses several sialic acid-containing oligosaccharide chains (s a o). The poly glutamic acid sequences (Glu)n are thought to constitute sites for cAp nucleation and binding sites with cAp. Binding sites for collagen and for cell attachment are also indicated. c Osteopontin (OPN) instead of (Glu)n, it contains a poly aspartic acid sequence (Asp)n that can interact with cAp and is thought to inhibit cAp crystal growth. After [60]