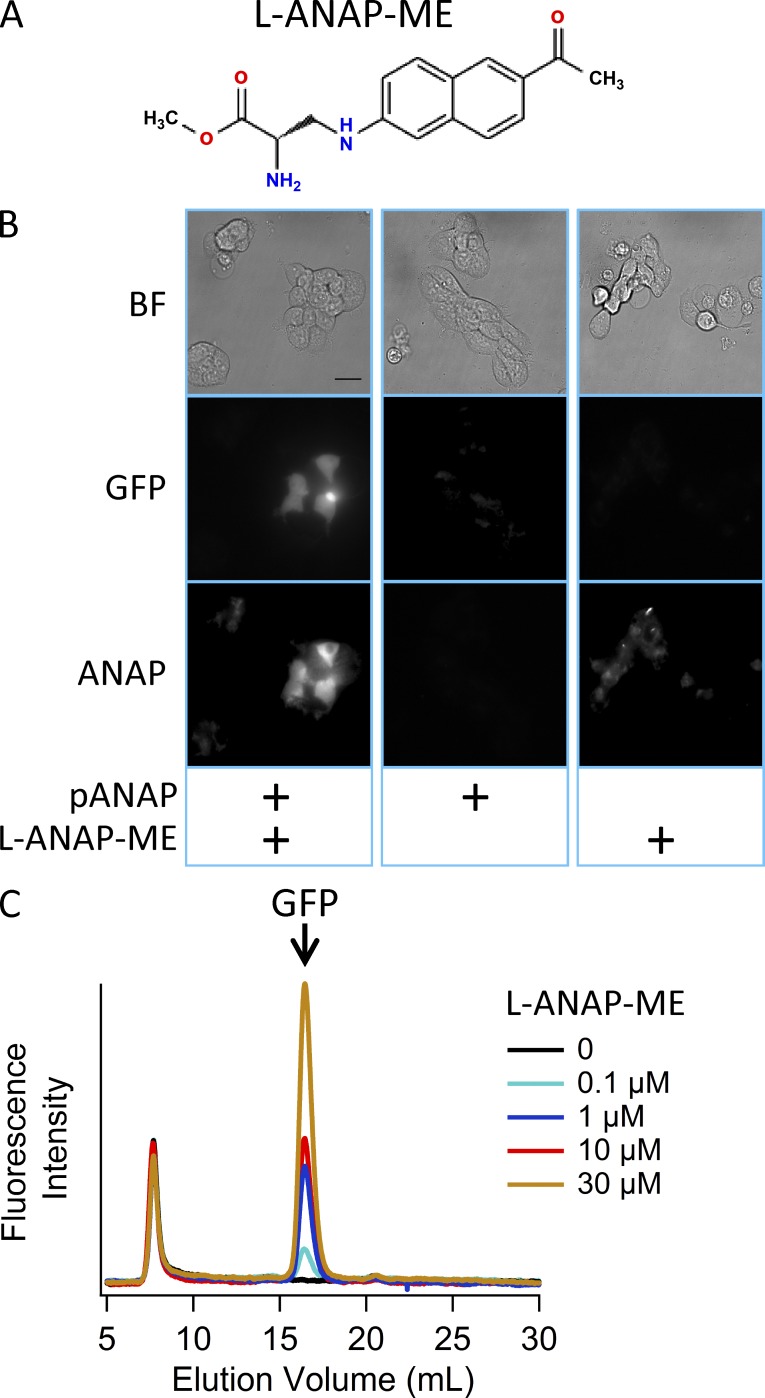
Figure 2.
Incorporation of the noncanonical amino acid L-ANAP into GFP. (A) The structure of L-ANAP-ME, the noncanonical amino acid used in this study. (B) Incorporation of L-ANAP into GFP-Y40TAG requires coexpression with pANAP and the addition of L-ANAP-ME to the culture medium. Each column shows the same field of cells taken using bright field (BF) microscopy (top), epifluorescent microscopy with an excitation/emission cube appropriate for GFP (middle), or epifluorescent microscopy with an excitation/emission cube appropriate for ANAP (bottom). All cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid encoding GFP-Y40TAG. Cells were cotransfected with pANAP and/or cultured in the presence of L-ANAP-ME as indicated at the bottom. For all images using the same cube, the camera settings and lookup tables used were identical. (C) Fluorescence detection size-exclusion chromatograph showing GFP fluorescence versus elution volume for cleared cell lysates generated from cells transfected with GFP-Y40TAG and pANAP and cultured with various concentrations of L-ANAP-ME. The earliest peak corresponds to the void volume of the column, and its presence in control samples not expressing GFP indicates that it is not a specific protein signal.