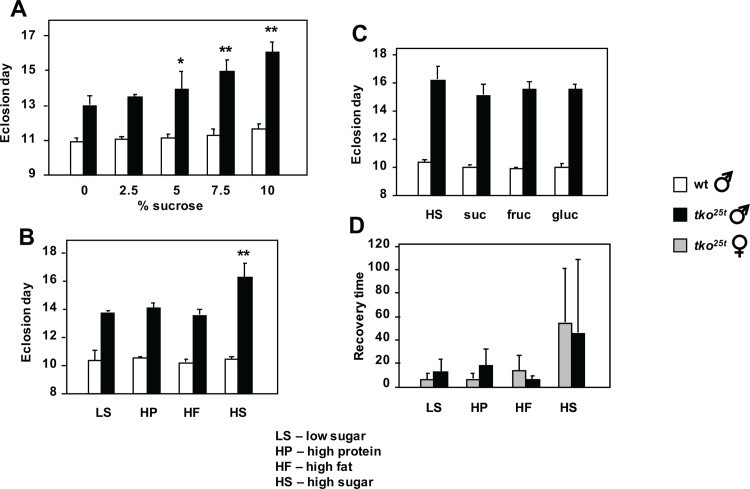
Fig 1. Modulation of tko25t phenotype by diet.
(A-C) Time to eclosion and (D) recovery time from mechanical shock (bang-sensitivity) of tko25t and wild-type flies grown on media of the indicated composition (see SI for details). In (A) asterisks denote data classes significantly different from flies of the same genotype grown on 0% sucrose medium (Student’s t test, * showing p < 0.05, ** showing p < 0.01). In (B) asterisks (**) denote significant difference from flies of the same genotype grown on all other media tested (Student’s t test, p < 0.01), which were not significantly different from each other. In (C) there were no significant differences from flies of the same genotype, grown on other media (Student’s t test, p > 0.05). In all experiments eclosion times for tko25t flies were also significantly different from those of wild-type flies grown on the same medium (Student’s t test, p < 0.01). In (D), the wide variance inherent to the phenotype precludes a standard statistical analysis. For corresponding eclosion data of females see Panel A in S1 Fig.