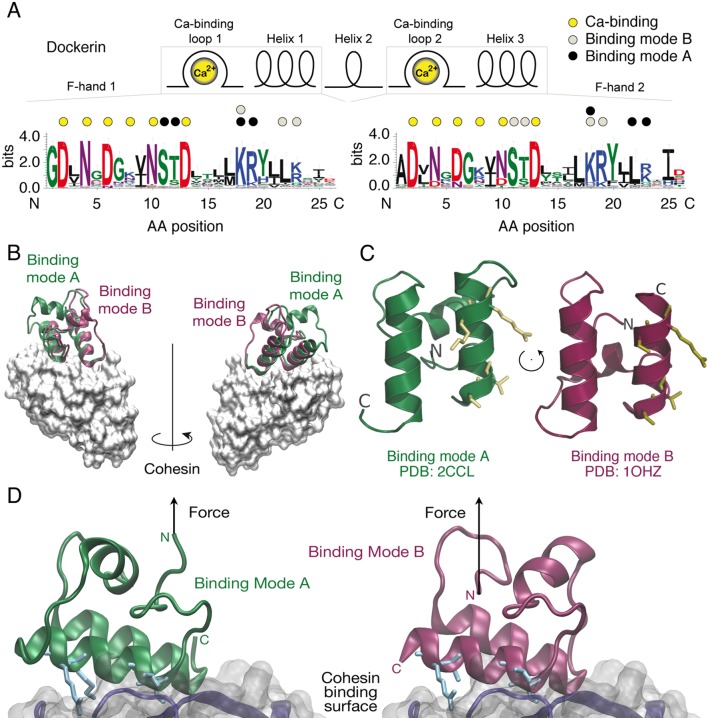
Figure 1. Cohesin:Dockerin dual binding modes.
(A) Secondary structure and consensus sequence logo (Crooks, 2004) assembled from 65 putative Ct type-I Doc variants. Dots above the amino acid codes indicate residues involved in: Ca2+ coordination (yellow), mode A binding (black), and mode B binding (gray). Letter colors represent chemical properties: Green, polar; purple, neutral; blue, basic; red, acidic; black, hydrophobic. Crucial Coh-binding residues are located at positions 11, 12, 18, 19, 22, and 23 in each F-hand motif. (B) Coh:Doc complex crystal structures showing overlaid Doc domains in the two binding modes. Images were generated by aligning the Coh domain (gray) from PDB 2CCL (green, binding mode (A) and 1OHZ (red, binding mode (B) using the VMD plugin MultiSeq (Humphrey et al., 1996; Roberts et al., 2006). (C) View of the Doc binding interface for each mode from the perspective of Coh. The conserved binding residues at positions 11, 12, 18, and 19 in the F-hand motif relevant for binding in the corresponding mode are depicted as stick models (yellow). (D) Close-up view of the interface for each binding mode with arrows indicating the location and direction of applied force. Binding residues 11, 12, 18, and 19 for binding mode A and 45, 46, 52, and 53 for binding mode B are shown as blue stick models. The Coh domain is oriented the exact same way in both views.