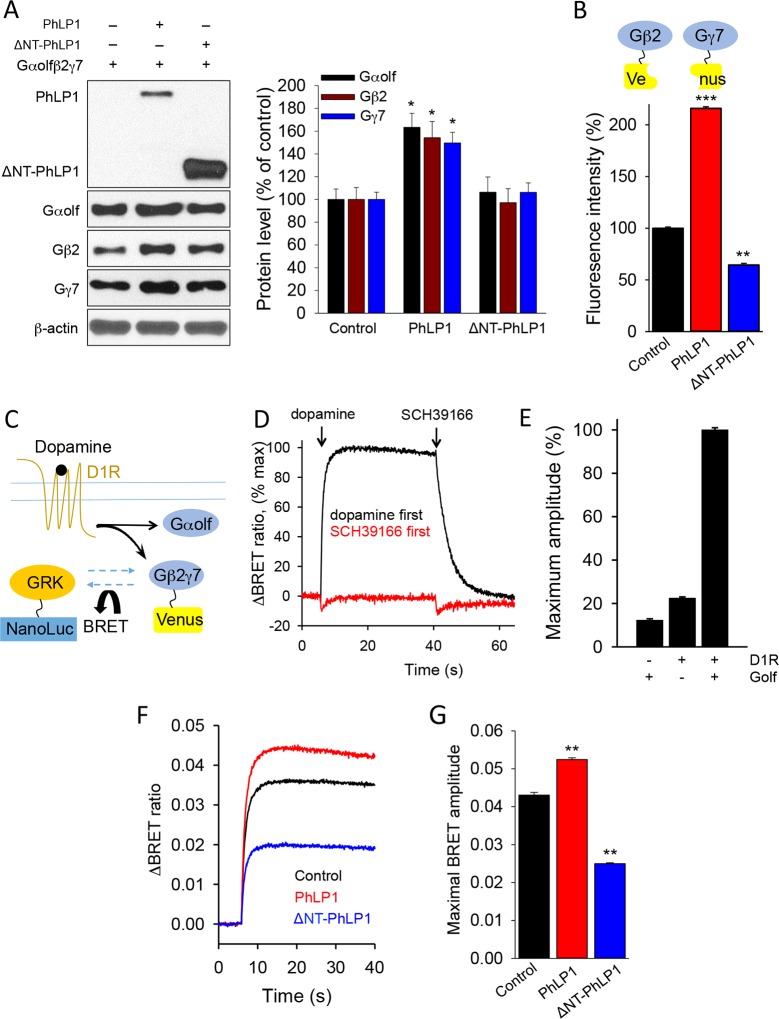
Figure 2. PhLP1 facilitates functional assembly of Gαolfβ2γ7 complex.
(A) Left, Full length of PhLP1 but not its N terminally truncated mutant ΔNT-PhLP1 increases the expression level of Gαolfβ2γ7 subunits upon overexpression in HEK293 cells. Right, quantification of immunoblot data from 3 independent experiments. Data were normalized to the individual protein expression in the control group without PhLP1 transfection. Data were analyzed by One-Way ANOVA (Gαolf F[2, 9] = 8.731, p = 0.008; Gβ2 F[2, 9] = 6.688, p = 0.017; Gγ7 F[2, 9] = 11.107, p = 0.004). *p<0.01 compared to the control group post hoc Tukey’s test. (B) Full length PhLP1 facilitates, while ΔNT-PhLP1 inhibits Gβ2γ7 assembly. Venus fluorescence intensity was used as a readout of Gβ2γ7 complex assembly in a complementation experiment in transfected HEK293 cells. Data were analyzed by One-Way ANOVA (F[2, 15] = 2719.521, p<0.001). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared with the control group, post hoc Tukey’s test. (C) Schematic diagram of BRET sensor strategy for examining the dissociation and reassociation of Gαolf and Gβ2γ7 subunits upon D1Rs activation and inactivation. (D) Representative BRET response traces. Cells transfected with D1R and Golf were stimulated by 100 μM dopamine followed by 100 μM SCH39166 (black) or by 100 μM SCH39166 followed by 100 μM dopamine (red). First and second ligands were applied at 5 and 40 s, respectively. (E) Control experiments examining the requirement of both Golf and D1R to transduce the signal. Cells were transfected with the three different conditions, Golf only, D1R only, or D1R plus Golf. Each bar represents the mean of 6 replicates. (F) Representative BRET signal traces in response to D1 receptor activation with dopamine (100 μM). (G) Comparison of maximal BRET ratios. Data were analyzed by One-Way ANOVA (F[2, 9] = 706.655, p<0.001). **p<0.01 compared with the control group, post hoc Tukey’s test.