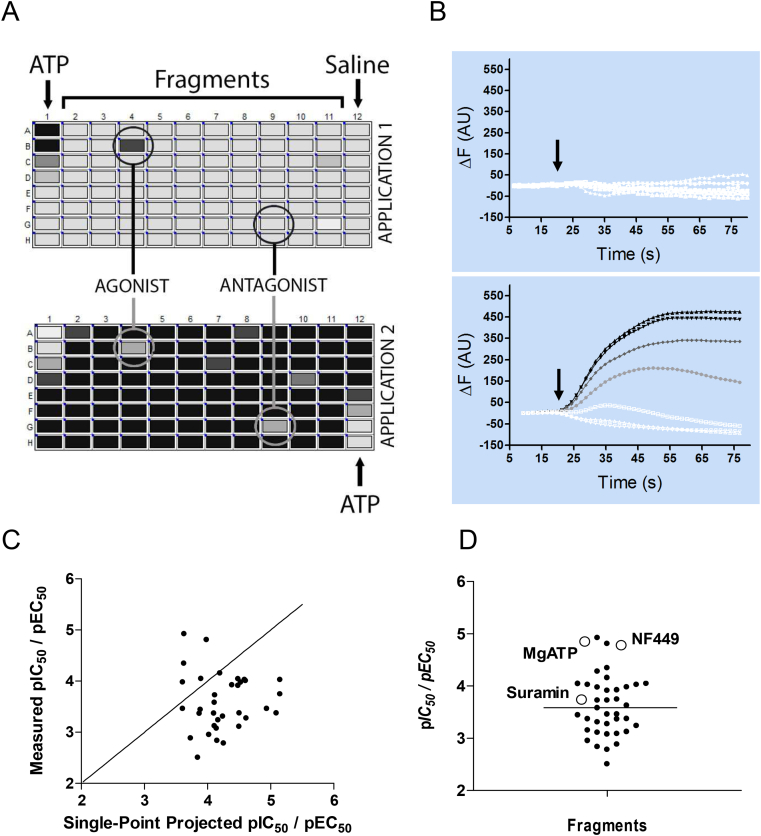
Fig. 1.
Typical data from fluorescent microplate assays using stably expressed doxycycline-inducible P2X1 receptors in a HEK 293T cell line. (A) An ATP concentration–response is included in column 1 of application 1, while column 12 contains saline alone. For hit screening 300 μM of different fragments are added to each well in columns 2–10. Because column 12 of application 1 contains saline alone, an ATP concentration–response can be performed on the same cells during application 2; ATP concentration–response curves at the start and end of the experiment can then be compared to confirm the consistency of the responses throughout the experimental period. To make visualisation of large datasets simpler, peak fluorescent responses are binned and assigned colours by the acquisition software, ranging from the largest fluorescence change (Black) to the smallest (white). Fragments are defined as agonists, antagonist, or inactive depending upon the responses to the two applications; see the methods section for a description. (B) The top panel shows a lack of fluorescent response following the addition of varying concentrations of ATP (arrow) to uninduced HEK 293T cells. The bottom panel shows raw data from an identical ATP application (arrow) on doxycycline-induced HEK 293T cells. The data in the bottom panel is from column 1 of Fig. 1A, plotted as a change in fluorescence over time. In both panels a baseline is recorded for 20 s before the addition of ATP. Such data can be used to plot concentration–dependence curves similar to those shown in Fig. 2. When hit fragments are identified at a single (300 μM) concentration, their concentration–dependence can be later assessed using the same experimental protocol as the ATP standards shown here. Although P2X1 receptors desensitise rapidly when measured using electrophysiological techniques, the fluorometric method shown here has much longer lasting responses as the cells are not voltage-clamped (depolarisation is longer lived); similar long-lived responses are seen for the rapidly desensitising 5-HT3 receptor when using the same dye (Price and Lummis, 2005). (C) A comparison of pIC50 values estimated from single-point measurements (300 μM) and those calculated from concentration-dependence curves. The straight line shows the vector along which the single-point predictions and measured potencies would be equal. (D) A comparison of pIC50 values determined for identified hit fragments (closed circles), ATP (open circle) and the established P2X1 antagonists, NF449 and suramin (open circles). Each point represents a different compound and the average affinity of all the fragments is shown as a horizontal bar.