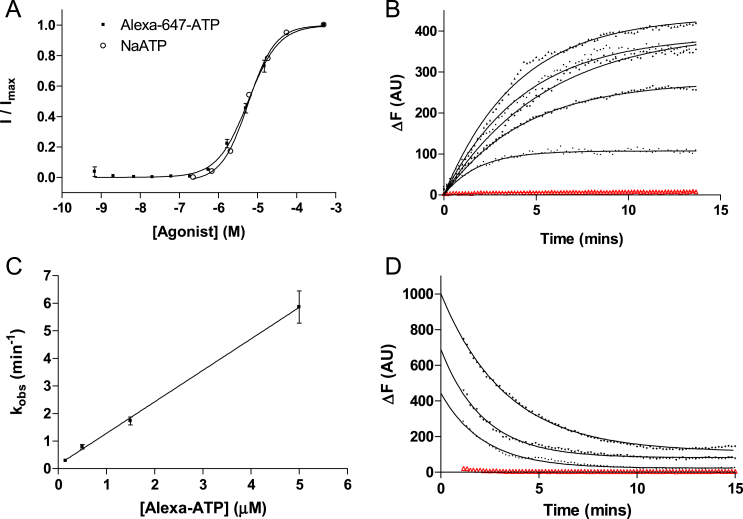
Fig. 3.
Kinetics of Alexa-647-ATP interactions at P2X1 receptors. (A) Alexa-647-ATP shows the same concentration-dependence as NaATP when measured using the voltage-sensitive dye. (B) Using confocal microscopy, the association of Alexa-647-ATP was determined by measuring the increase in cell-surface fluorescence following the application of different concentrations of this ligand. Upon application of Alexa-647-ATP a saturable increase in fluorescence was observed and was best fitted with a mono-exponential curve to yield kobs (see Table 1). In this example the change in fluorescence following the addition of 0.3 μM Alexa-647-ATP is shown for both the background (red) and for five cells (black). (C) A plot of the average kobs against the concentration of Alexa-647-ATP was fitted by linear regression (R2 = 0.89) to give the rates of association (slope) and dissociation (intercept at y = 0). The affinity of Alexa-647-ATP was calculated using these kinetic values (Eq. (3)) and gave a Kd of 119 nM. (D) Dissociation was measured after rapidly washing Alexa-647-ATP equilibrated P2X1-expressing HEK 293T cells with fresh PBS (t = 0). Dissociation was best-fitted with mono-exponential fits that gave an average dissociation rate (koff = 0.40 min−1) that was similar to the value calculated in panel (C). Similar to panel A, there is low background fluorescence (red) when compared to cell-surface fluorescence (black).