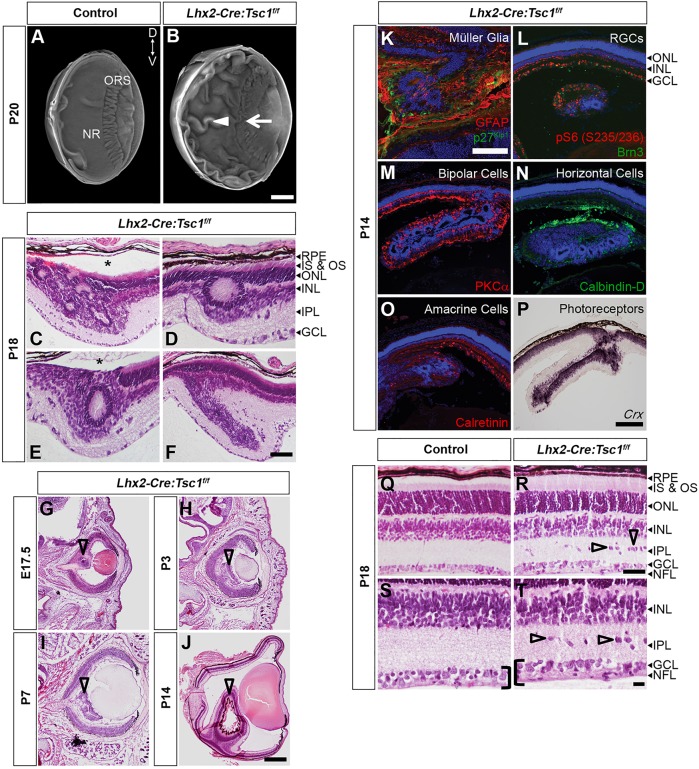
Fig. 2.
Conditional deletion of Tsc1 leads to enlarged eyes, hamartomas and loss of retinal architecture. (A,B) OPT 3D volume rendering from control (A) and Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f (B) mice, showing an enlargement of the eye, retinal folding (arrowhead) and loss of ora serrata (ORS) integrity (arrow) in Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f mice. (C-F) Histological analysis of coronal eye sections demonstrating that the retinal folds observed during OPT analysis of Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f mice are hamartomas that were organised into ring heterotopias. Moreover, retinal detachment was a common occurrence in areas of hamartoma formation (C,E, asterisks). (G-J) Histological analysis of coronal eye sections demonstrating that hamartomas first become evident during late embryogenesis (G, arrowhead) in Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f mice. These lesions then become more pronounced during postnatal development (H-J, arrowheads). (K-P) Immunostaining and in situ hybridisation analyses demonstrating that hamartomas in Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f mice are enriched in pS6 (S235/236) protein (L) and consist of all the cellular classes that populate the retina: Müller glia (K, GFAP+, p27Kip1+), RGCs (L, Brn3+), bipolar cells (M, PKCα+), horizontal cells (N, calbindin-D+), amacrine cells (O, calretinin+) and photoreceptors (P, Crx+). (Q-T) Histological analysis of coronal eye sections from control (Q,S) and Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f (R,T) mice demonstrate the irregular ordering of the INL, an IPL populated with ectopic cells (R,T, arrowheads) and a widening of the GCL and NFL (S,T, brackets) in Lhx2-Cre:Tsc1f/f mice. Scale bars: (A,B,G-J) 500 µm; (C-F,Q-T) 50 µm; (K) 100 µm; (L-P) 200 µm. Abbreviations: Brn, brain-specific homeobox; Crx, cone-rod homeobox; D, dorsal; GCL, ganglion cell layer; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; IPL, inner plexiform layer; IS, inner segments; INL, inner nuclear layer; NFL, nerve fiber layer; NR, neural retina; ORS, ora serrata; OS, outer segments; PKC, protein kinase C; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; V, ventral.