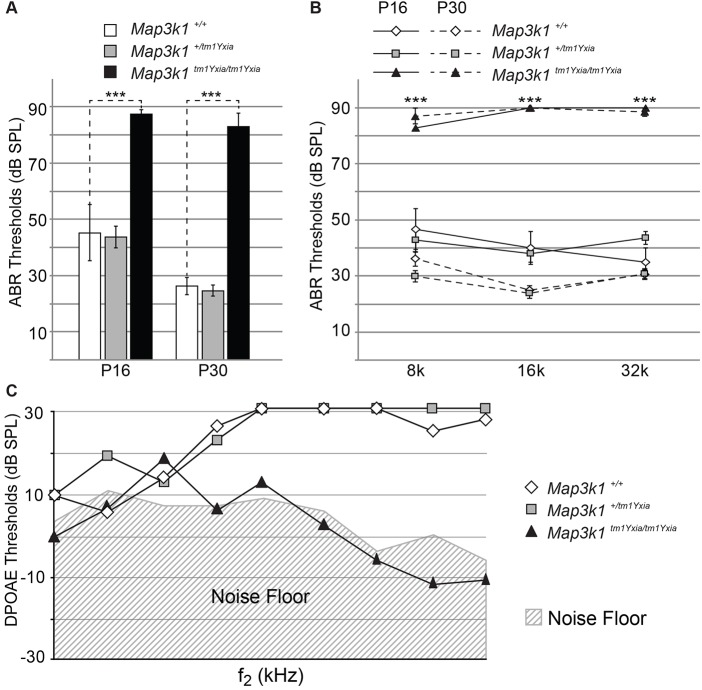
Fig. 4.
Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant mice have elevated hearing thresholds. Hearing thresholds of 3 wild-type, 7 heterozygous and 8 Map3k1tm1Yxia homozygous mice were evaluated at P16, whereas 8 wild-type, 11 heterozygous and 7 Map3k1tm1Yxia homozygous mice were tested at P30. (A) Averaged auditory brainstem responses (ABR) thresholds of wild-type, and heterozygous and homozygous Map3k1tm1Yxia mice at P16 and P30 in response to click stimulus. The Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant mice showed significantly (***P<0.001) elevated thresholds compared with heterozygous and wild-type mice at both ages (mean±s.e.m.). (B) Averaged ABR thresholds of wild-type (white diamonds), heterozygous (gray squares) and homozygous Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant (black triangles) mice at P16 (solid lines) and P30 (dashed lines), in response to 8-kHz, 16-kHz and 32-kHz tone-bursts. At both developmental stages, Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant mice showed significantly (***P<0.001) elevated thresholds compared with the wild-type control and heterozygous mice at all frequencies tested (mean±s.e.m.). (C) Distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs) of Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant (black triangles), heterozygous (gray squares) and wild-type control (white diamonds) mice at P30, represented as a function of f2 stimulus frequencies. Map3k1tm1Yxia mutant mice showed no responses, with values close to the noise floor, indicating that the residual OHCs were non-functional. SPL, sound pressure level.