Fig. 5.
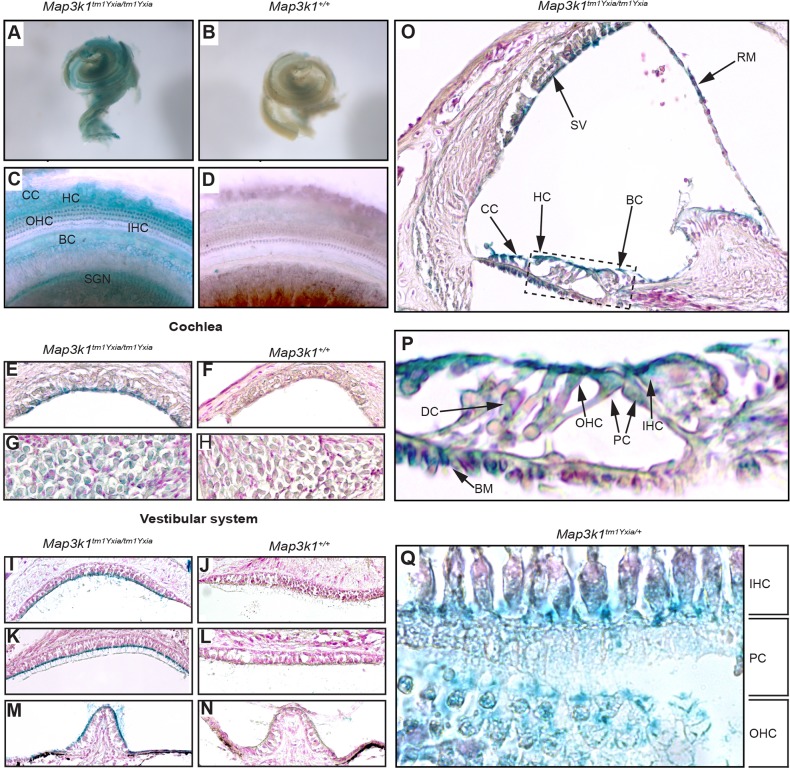
Map3k1–β-galactosidase expression in the inner ear of P12 Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia and Map3k1tm1Yxia/+ mice. (A,B) X-Gal-stained cochleae from Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia and Map3k1+/+ mice, respectively. The Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia cochlea (A) shows widespread staining owing to the presence of a MAP3K1–β-galactosidase fusion protein in these mice. (C,D) Extended focus images showing staining in the cochlear duct. In Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia cochlea (C), strong staining can be observed in Claudius cells (CC), Hensen cells (HC), outer hair cells (OHC), inner hair cells (IHC), border cells of the internal spiral sulcus (BC) and spiral ganglion neurons (SGN). This staining is not observed in the Map3k1+/+ cochlea (D). (E-N) X-Gal-stained sagittal sections of the cochleae and vestibular systems from Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia and Map3k1+/+ mice: (E,F) stria vascularis, (G,H) spiral ganglion neurons, (I,J) sacular macula, (K,L) utricular macula, (M,N) crista ampularis. X-Gal-positive staining is present in the marginal cells of the stria vascularis (E), the spiral ganglion neurons (G) and the apical surfaces of supporting cells and hair cells in all of the otolithic organs in the vestibular system of Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia mice. (O) Shows the distribution of MAP3K1–β-galactosidase in the cochlear duct of Map3k1tm1Yxia/tm1Yxia mice. Staining is observed in the stria vascularis (SV), Reissner's membrane (RM), Claudius cells (CC), Hensen cells (HC) and border cells of the internal spiral sulcus (BC). (P) An enlargement of the organ of Corti (dashed box in panel O), showing MAP3K1–β-galactosidase expression in the apical surface of IHC, OHC, Deiters' cells (DC), pillar cells (PC) and tympanic border cells of the basilar membrane (BM). (Q) Transverse section of the organ of Corti from a Map3k1tm1Yxia/+ mouse, highlighting more clearly X-Gal-positive staining in the IHCs, PCs and OHCs.