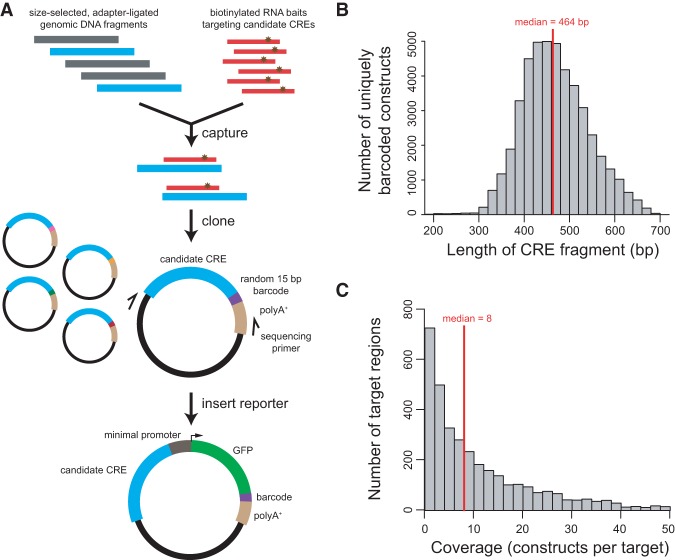
Figure 1.
“Capture-and-clone” allows synthesis of CRE-seq libraries with long CREs. (A) Schematic of the capture-and-clone approach. Size-selected, adapter-ligated genomic DNA was hybridized to biotinylated RNA baits that tiled across candidate CRE regions of interest. Captured fragments were cloned into a barcoded vector library with unique 15-mer barcodes. Paired-end sequencing revealed the CRE-barcode correspondence. A minimal promoter-GFP reporter cassette was subsequently cloned into the library. (B) Histogram showing the distribution of the lengths of captured fragments that were cloned into the barcoded vector library, based on paired-end sequencing. The median length was 464 bp. (C) Histogram showing the distribution of target coverage, i.e., the number of captured fragments that overlapped a 300-bp target region. Of the 4000 targeted regions, 3483 regions were represented by at least one construct. The median coverage among represented regions was 8. Not shown in graph: 517 nonrepresented regions and 114 target regions with a coverage of more than 50.