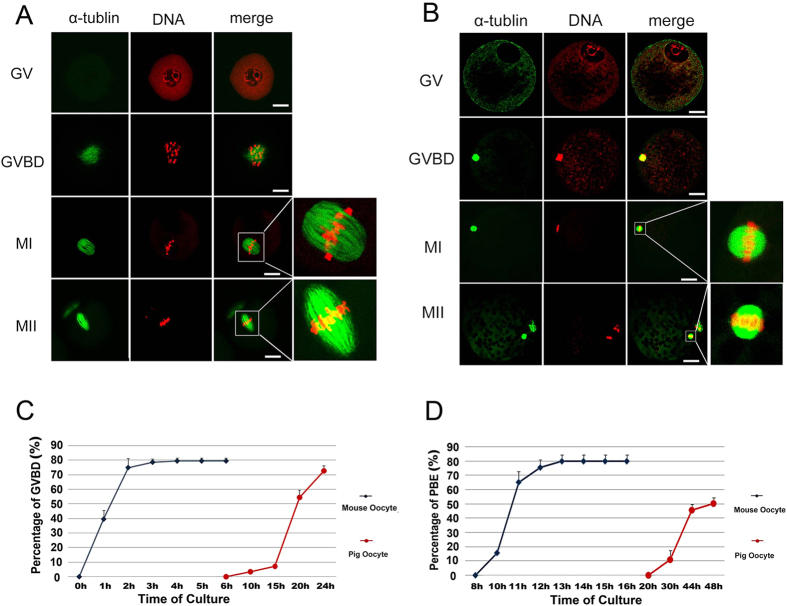
Figure 2. Overview of the difference in spindle size and in vitro maturational time course in pig and mouse oocytes.
(A) Mouse oocytes at the GV, GVBD, MI and MII stages were stained with PI and anti-α-tublin antibody to detect mouse meiotic spindle shape and size. (B) Pig oocytes at the GV, GVBD, MI and MII stages were stained with PI and anti-α-tubulin antibody to detect pig meiotic spindle shape and size. (C) Percentages of mouse oocyte GVBDs (0 h: 0%; 1 h: 39.53 ± 6.10%; 2 h: 74.49 ± 6.26%; 3 h: 78.57 ± 2.18%; 4 h: 79.41 ± 2.03%; 5 h: 79.41 ± 2.03%; 6 h: 79.41 ± 2.03%) were observed each hour from 0–6 h of in vitro culture, and percentages of pig oocyte GVBDs (6 h: 0%; 10 h: 3.53 ± 1.22; 15 h: 7.11 ± 1.24; 20 h: 54.44 ± 5.09; 24 h: 72.67 ± 3.48) were observed at 6 h, 10 h, 15 h, 20 hand 24 h of in vitro culture. (D) Percentages of mouse oocytes with first polar body extrusion (8 h: 0%; 10 h: 15.70 ± 0.93%; 11 h: 65.22 ± 7.25%; 12 h: 75.56 ± 5.18%; 13 h: 79.94 ± 4.38%; 14 h: 79.94 ± 4.38%; 15 h: 79.94 ± 4.38%; 16 h: 79.94 ± 4.38%) were observed one or two hours from 8 h to 16 h of in vitro culture, and percentages of pig oocytes with first polar body extrusion (20 h: 0%; 30 h: 11.01 ± 6.27%; 44 h: 45.55 ± 3.85%; 48 h: 50.14 ± 4.07%) were observed at 20 h, 30 h, 44 hand 48 h of in vitro culture (bar = 30 μm).