Figure 5.
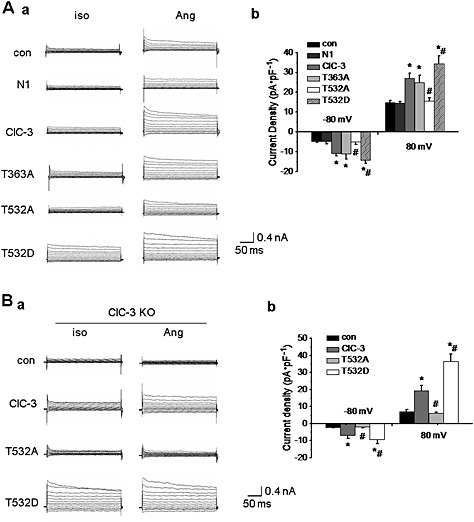
Phosphorylation of Thr532 in ClC‐3 protein was required for AngII‐induced Cl− current. A. The effect of ClC‐3 site mutations on AngII(1 μmol·L−1)‐induced Cl− current in A10 cells. a. Representative traces of Cl− current in A10 cells transfected with EGFP‐N1 (N1), WT ClC‐3, ClC‐3 T363A (T363A), ClC‐3 T532A (T532A) and ClC‐3 T532D (T532D) plasmids for 48 h. Compared with WT ClC‐3 channels, the current density was not altered by the T362A mutation, while the T532A mutation significantly reduced the current density. Moreover, the T532D mutation markedly increased the current density compared with WT ClC‐3 channels. b. Bar chart from the experiments at −80 mV (downward bars) and +80 mV (upward bars) in con, N1‐transfected, ClC‐3‐transfected, T363A‐transfected, T532A‐transfected, and T532D‐ transfected cells (n = 6, *P < 0.05 vs. con, #P < 0.05 vs. ClC‐3). B. The effect of Thr532 phosphorylation on AngII(1 μmol L−1)‐induced Cl− current in ClC‐3 null BASMC (KO). a. Representative traces of Cl− current in ClC‐3 null BASMC transfected with WT ClC‐3, T532A and T532D plasmids for 48 h. AngII could not induce a Cl− current in cells transfected with T532A plasmid, while AngII‐induced Cl− current was observed in cells transfected with WT ClC‐3 plasmid, which was further potentiated in cells transfected with T532D plasmid. b. Bar chart from the experiments at −80 mV (downward bars) and +80 mV (upward bars) in ClC‐3 null BASMC transfected with ClC‐3, T532A and T532D plasmids. n = 6, *P < 0.05 vs. con, #P < 0.05 vs. ClC‐3.
