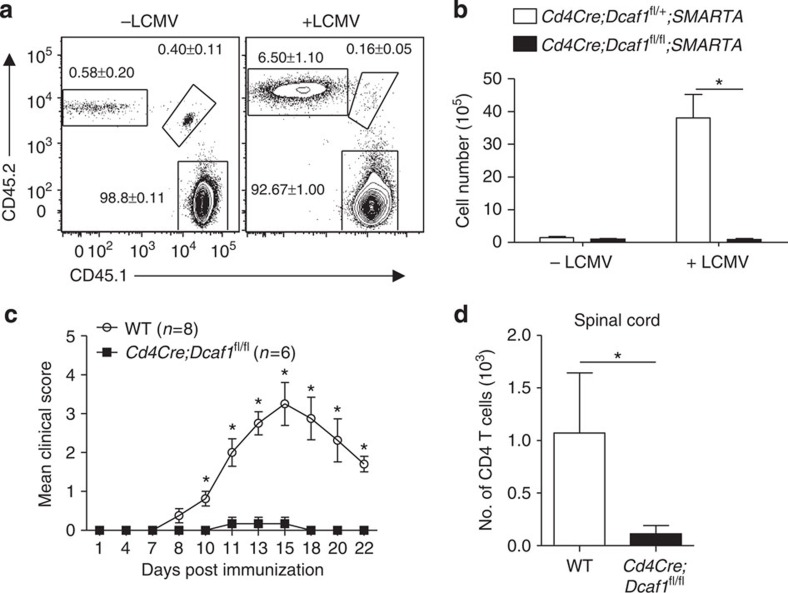
Figure 5. DCAF1 controls T-cell response during viral infection and autoimmunity.
(a,b) 1 × 106 of CD4+ T cells isolated from Cd4Cre;Dcaf1fl/+;SMARTA mice (CD45.2+) and Cd4Cre;Dcaf1fl/fl;SMARTA mice (CD45.1+CD45.2+) were mixed and transferred into syngeneic wild-type recipient mice (CD45.1+) followed by LCMV infection (+LCMV) or remain uninfected (−LCMV). The percentages (a) and the numbers (b) of donor cells of different genotypes were determined by flow-cytometry 5 days after infection. Representative results and means±s.d. of 10 mice of 2 experiments are shown (*P<0.05 by Student's t-test). (c,d) Wild-type (WT) (n=8) and Cd4Cre;Dcaf1fl/fl (n=6) mice were injected with MOG/CFA to elicit autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). The disease clinic scores were recorded at indicated time points. Means±s.d. are shown (c) (*P<0.05 by Mann–Whitney's U-test). The numbers of spinal cord infiltrating CD4+ T cells were assessed 22 days post EAE elicitation. Means±s.d. are shown (d) (*P<0.05 by Student's t-test).