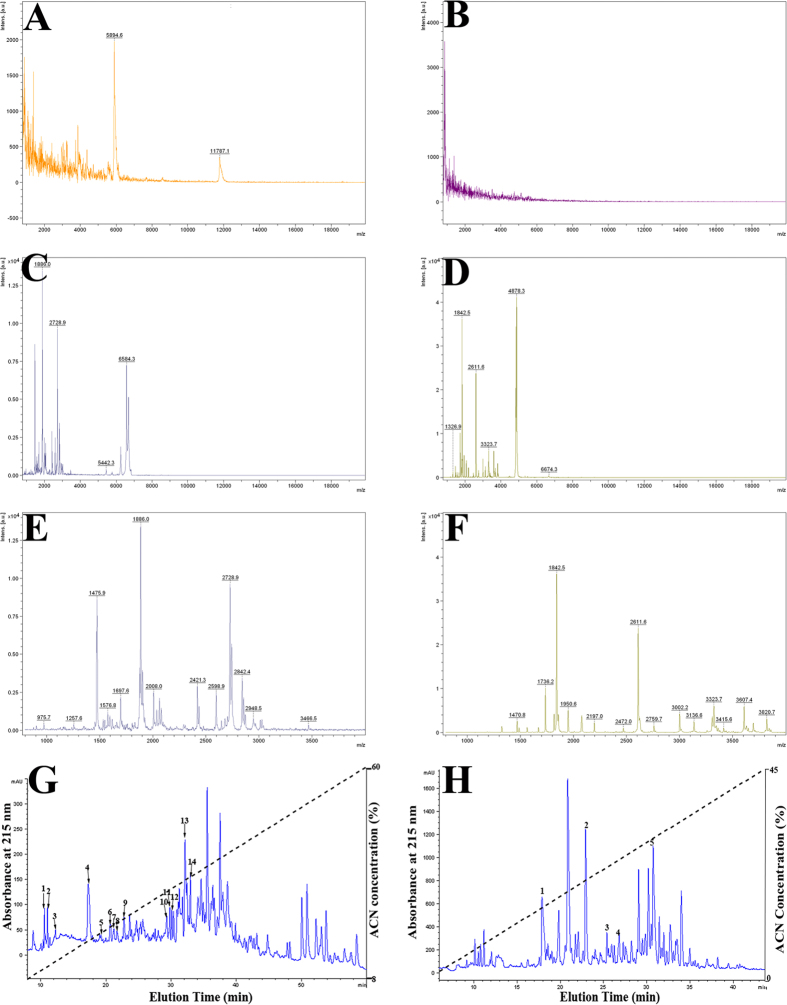
Figure 3. Overview of peptides induced by UV radiation.
MS and HPLC analyses showed that UV radiation induced the secretion of many peptides compared with the controls. Left O. andersonii and right O. wuchuanensis. (A) MS analysis of O. andersonii skin secretions without UV exposure. (B) MS analysis of O. wuchuanensis skin secretions without UV exposure. (C) MS analysis of O. andersonii skin secretions with UV exposure, molecular weight range 800–20000 Da. (D) MS analysis of O. wuchuanensis skin secretions with UV exposure, molecular weight range 800–20000 Da. (E) MS analysis of O. andersonii skin secretions with UV exposure, molecular weight range 800–4000 Da. (F) MS analysis of O. wuchuanensis skin secretions with UV exposure, molecular weight range 800–4000 Da. (G) First RP-HPLC purification step of AOPs from skin secretions of O. andersonii. Skin secretions were applied to a C18 RP-HPLC column pre-equilibrated with 0.1% (v/v) TFA in water, and elution was achieved by a linear gradient (0–100% in 100 min) of 0.1% (v/v) TFA in ACN at a flow rate of 1 mL/min and was monitored at 215 nm. Fourteen peaks with ABTS+ scavenging activity were further purified. (H) First RP-HPLC purification step of AOPs from skin secretions of O. wuchuanensis. Skin secretions were applied to a C18 RP-HPLC column pre-equilibrated with 0.1% (v/v) TFA in water, and elution was achieved by a linear gradient (0–100% in 100 min) of 0.1% (v/v) TFA in ACN at a flow rate of 1 ml/min and was monitored at 215 nm. Five peaks with ABTS+ scavenging activity were further purified.