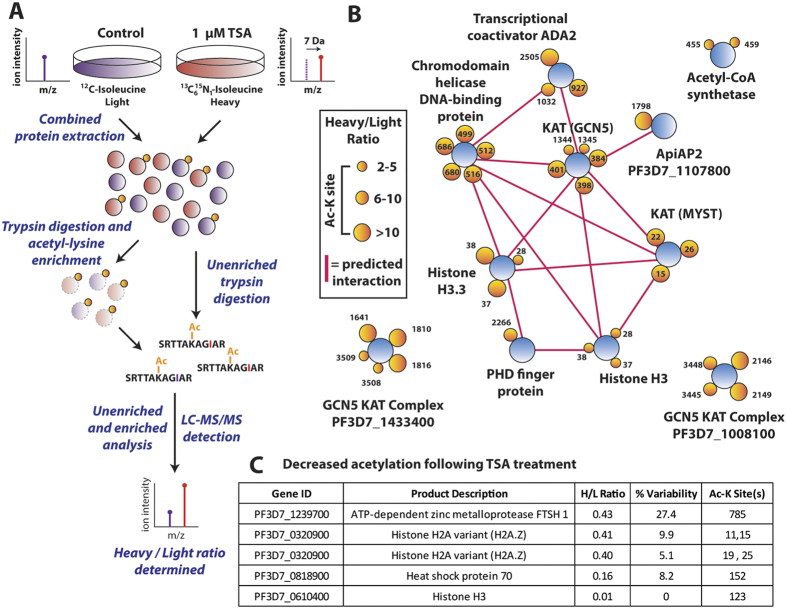
Figure 4.
(A) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture. P. falciparum infected erythrocytes are maintained under standard culturing conditions in RPMI containing either 12C614N1 isoleucine (light) or 13C615N1 isoleucine (heavy) for 72 hours. After proteome labeling (>95%), the light culture was untreated and the heavy culture was treated with 1 μM of tricostatin A (TSA) for three hours. Treated (heavy) and untreated (light) cultures were saponin-permeabilized, washed, combined and extracted. Following trypsin digestion and SCX fractionation, samples were analyzed both directly (unenriched) and subsequent to enrichment by anti-acetyl lysine immunoprecipitation via high resolution nano-UPLC-MS and MS/MS. Relative ratios of the isoleucine bearing heavy (+7 Da) peptides to their light counterparts were measured to determine the ratios of acetylation in the original experiments. (B) Proteins containing the acetyl-lysine sites that were quantified as undergoing a >2-fold increase (heavy/light ratio >2) when treated with TSA. Proteins are represented as blue circles, individual acetyl-lysine sites as orange circles (with the residue position defined alongside/within). The size of each acetyl-lysine site is proportional to the increase in acetylation following TSA treatment (quantified as the treated/untreated heavy/light ratio). Network analysis was performed on the entire dataset to represent functionally-related proteins. Direct (physical) or indirect (functional) interactions were defined with experimental, databases and text-mining information sources using STRING 9.1 with a medium confidence cutoff (0.4) and are represented by a pink line between proteins. (C) A subset of acetyl-lysine sites that decreased following TSA treatment (<0.5 heavy/light ratio). Percent variability is a measure of the heavy/light ratio variation between repeated measurements, where a value of 0 represents repeated measurement at the extreme minimum quantification range. The Ac-K site indicates the lysine residue position that underwent decreased acetylation. Supplemental Table 5 and 6 contain the complete list of altered acetylation sites under TSA treatment.