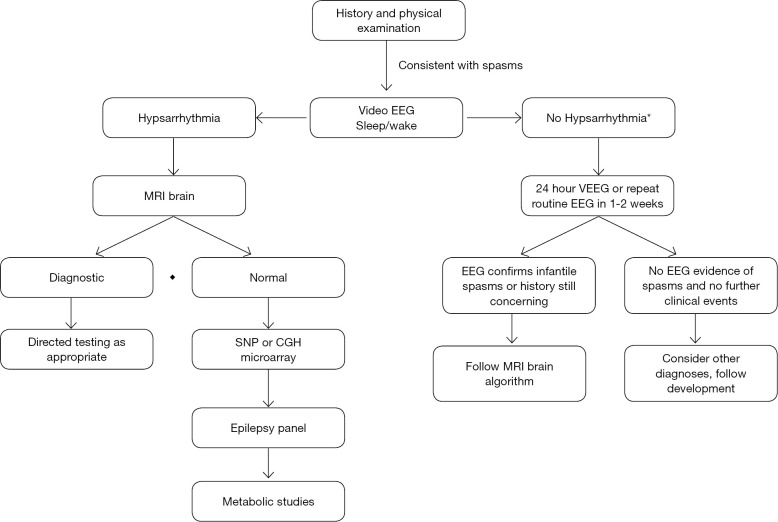
Figure 1.
Diagnostic algorithm for infantile spasms. As noted, imaging has the highest yield, followed by genetic studies. *, Patients with a convincing history of infantile spasms and abnormalities other than hypsarrhythmia on EEG, may proceed to imaging without repeat EEG. If the concern for infantile spasms is significant and development is affected, it is not recommended to wait for EEG abnormalities, as up to 1/3 of patients may not have hypsarrhythmia. Treatment should begin once imaging is complete unless there is concern for infection and other work-up is needed. EEG, electroencephalogram; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; ACTH, adrenocorticotrophic hormone; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; CGH, comparative genomic hybridization.