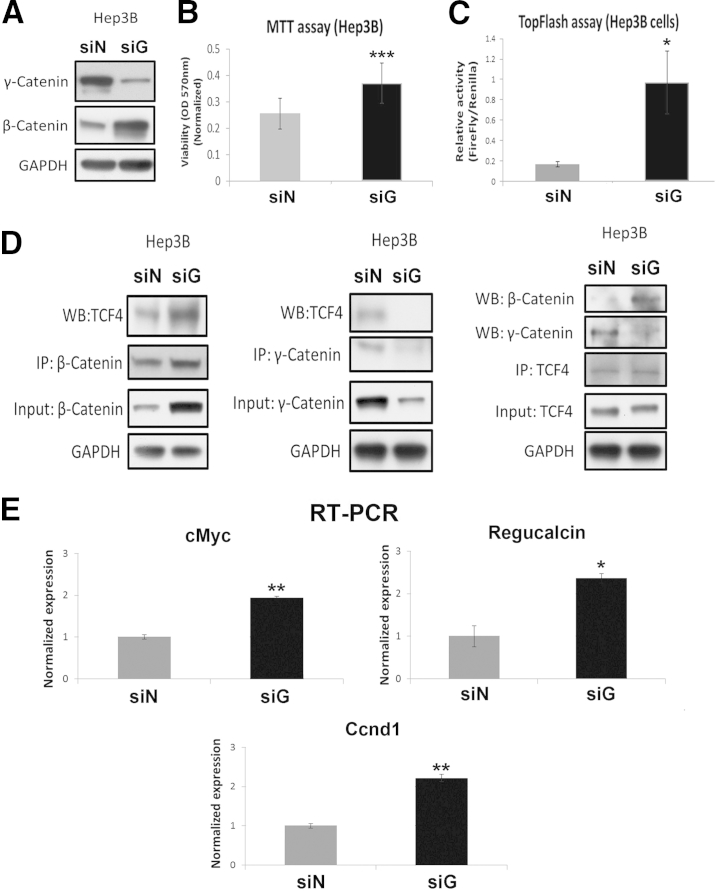
Figure 7.
In vitro suppression of γ-catenin in hepatocellular cancer cells leads to enhanced β-catenin activity. A: Representative Western blot (WB) shows successful knockdown of γ-catenin at 48 hours after γ-catenin siRNA (siG) compared with negative control siRNA (siN) transfection of Hep3B cells. A notable increase in β-catenin levels was evident in siG-transfected cells. B: MTT assay shows increased Hep3B cell viability at 48 hours after siG transfection compared with siN. C: TopFlash assay shows a significant increase in T-cell factor (TCF) activity in Hep3B cells at 48 hours after siG transfection (ratio of firefly/Renilla: siG = 0.97, siN = 0.17). D: Representative immunoprecipitation (IP) shows increased association of β-catenin and TCF4 in Hep3B cells after 48 hours of siG transfection compared with siN. γ-Catenin–TCF4 association is evident basally in siN-transfected Hep3B cells, which is abrogated after 48 hours’ transfection with siG. E: Real-time PCR shows a significant increase in mRNA expression of c-Myc, regucalcin, and cyclin-D1 (Cnnd1) in Hep3B cells in the siG-transfected group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.