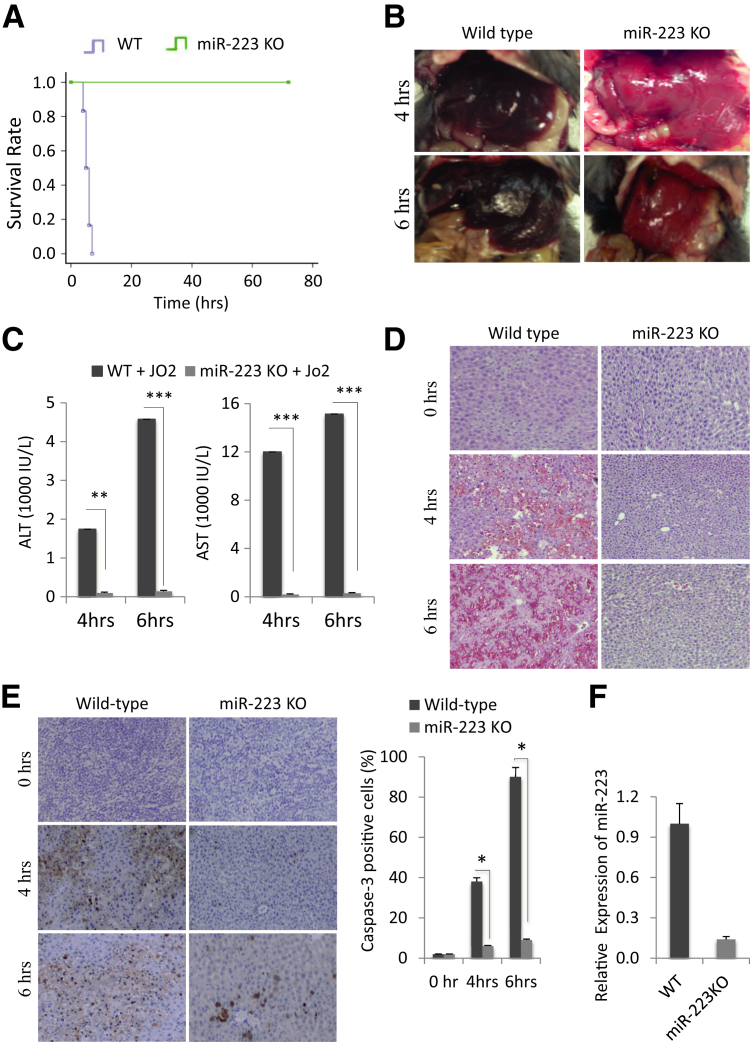
Figure 1.
Deletion of miR-223 prevents Fas-induced liver injury. A: Wild-type (WT) and miR-223 knockout (KO) mice were i.p. injected with 0.5 μg/g Jo2 per 1 g body weight, and the animal survival was recorded at hourly intervals. B: Gross images of livers from WT and miR-223 KO mice 4 and 6 hours after Jo2 injection. C: Serum transaminase levels [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)] from WT and miR-223 KO mice (4 and 6 hours after Jo2 treatment). Jo2-treated miR-223 KO mice show lower serum ALT and AST levels compared with Jo2-treated WT mice. D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver tissues from WT and miR-223 KO mice (0, 4, and 6 hours after Jo2 injection). E: Caspase-3 immunostaining of liver tissues from WT and miR-223 KO mice (0, 4, and 6 hours after Jo2 injection) and the percentages of caspase-3–positive cells. F: Relative fold expression of miR-223 in WT and miR-223 KO livers, as determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Data represent means ± SD of fold changes (C). N = 6 per group (A). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Original magnification, ×100 (D and E).