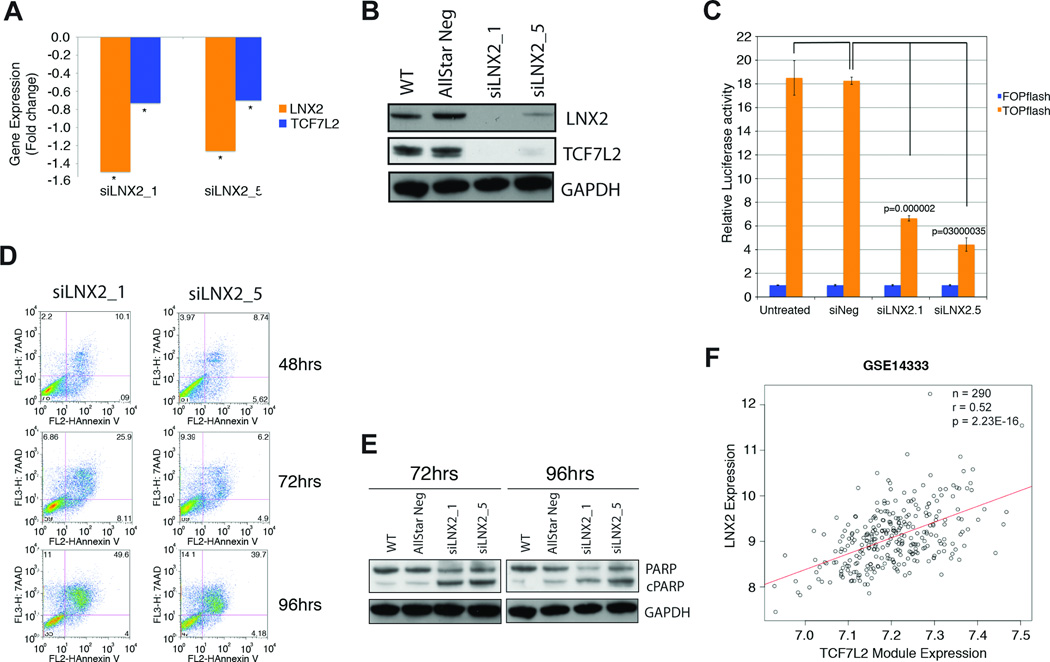
Figure 6. Functional and bioinformatic analysis of the role of LNX2 in CRC.
Confirmation of downregulation of LNX2 and TCF7L2 after silencing of LNX2 with two independent siRNAs by qRT-PCR. We observed significantly reduced expression of the transcription factor TCF7L2, both (A) on the RNA (* P<0.05) and (B) protein level. (C) Functional validation of reduced WNT/β-catenin signaling using the TOP-FOP-Flash reporter assay. Reduced expression of TCF7L2 results in markedly lower canonical WNT/β-catenin activity as measured using a TOP-FOP-Flash reporter assay after silencing LNX2 with two independent siRNAs. (D) Silencing of LNX2 with both siRNAs triggers increased apoptosis in SW480 cells as measured by Annexin V vs. 7-AAD using flow cytometry. The Annexin V positive cells at 96 hrs after transfection reached almost 50%. (E) Western blot analysis measuring cleaved PARP at two different time points, 72 and 96 hrs, confirmed an increased rate of apoptosis as a consequence of silencing LNX2 for both siRNAs. (F) Correlation of the expression of a module of genes regulated by the transcription factor TCF7L2 and downregulated signature genes after silencing LNX2 in a set of 290 primary colorectal cancer samples. Y-axis: expression levels of LNX2 in primary colorectal carcinomas; x-axis: expression levels of the TCF7L2 module. The correlation indicates a direct influence of LNX2 on the expression of TCF7L2-regulated genes and consequently the genomic amplification of chromosome 13 and activation of WNT-signaling.