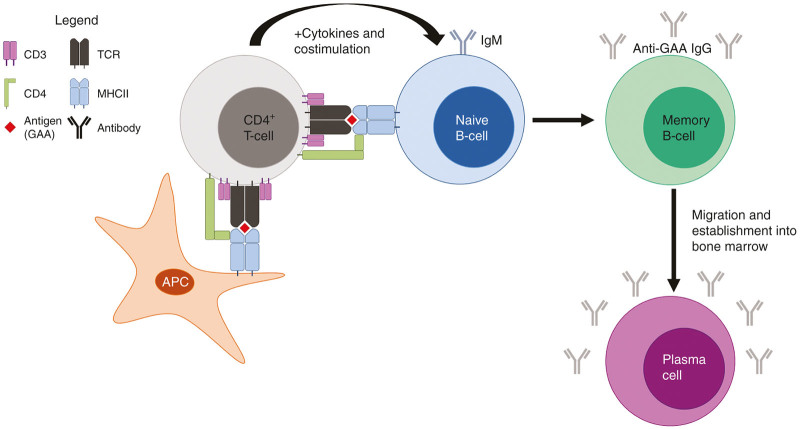
Figure 1.
Generation of a humoral immune response. CD4+ T-cells engage MHCII loaded with antigen (GAA) on APCs or naive B-cells via TCR. The CD4 coreceptor also binds and facilitates the appropriate signaling through CD3. During the immune response, additional cytokines and costimulatory molecules drive the generation of memory B-cells which undergo Ig class switching from immature IgM to affinity matured IgGs directed against the antigen. Memory B-cells then migrate into the bone marrow and develop into antigen-specific plasma cells which perpetually produce antibodies. APC, antigen-presenting cell; GAA, acid α-glucosidase; Ig, immunoglobulin; MHCII, major histocompatibility complex II; TCR, T-cell receptor.