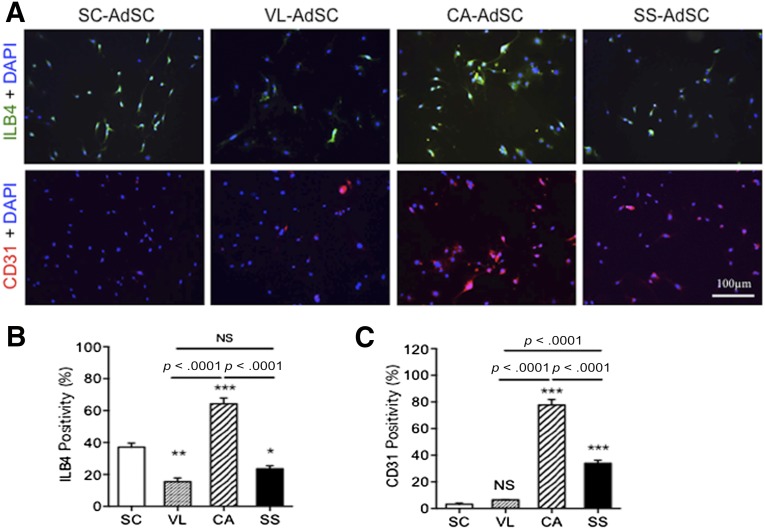
Figure 3.
Endothelial differentiation in AdSCs from four different adipose tissues by fluorescent immunocytochemistry. (A): To assess which source of AdSCs could differentiate into endothelial cells, the cells were stained with anti-ILB4 (green) and anti-CD31 (red) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B, C): The rate of ILB4-positive (B) and CD31-positive (C) cells was compared among the AdSCs from four different adipose tissues. ∗, p < .05; ∗∗, p < .01; ∗∗∗, p < .001; NS, not significant vs. SC. All experiments were performed in triplicate and statistically analyzed. Abbreviations: AdSCs, adipose-derived stem cells; CA, cardiac brown adipose tissue; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; ILB4, isolectin-B4; NS, not significant; SC, subcutaneous white adipose tissue; SS, subscapular brown adipose tissue; VL, visceral white adipose tissue.