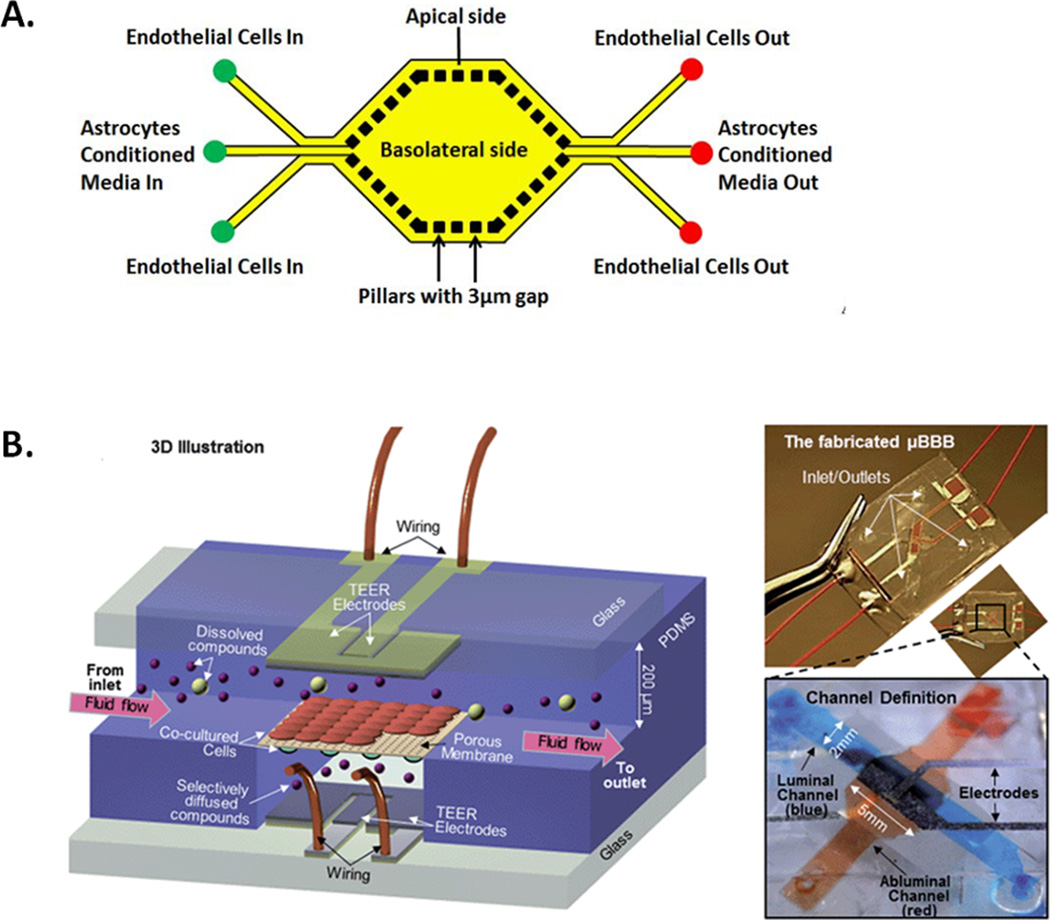
Figure 2. Microfluidic BBB models.
Examples of experimental microfluidic devices designed to model the BBB A) Diagram showing a top view of the SyM-BBB microfluidic BBB model. Micro-pillars are used to separate a basolateral central reservoir to which astocytes or astrocyte-conditioned media is added. BECs are seeded in the peripheral channels whilst the micropillars allow basolateral interaction.51 B) The µBBB model, uses a porous membrane to separate basolateral cells from BECs, inbuilt electrodes allow for TEER measurement across the BEC monolayer50. (Reproduced in part from Ref 51 and Ref 50 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry)