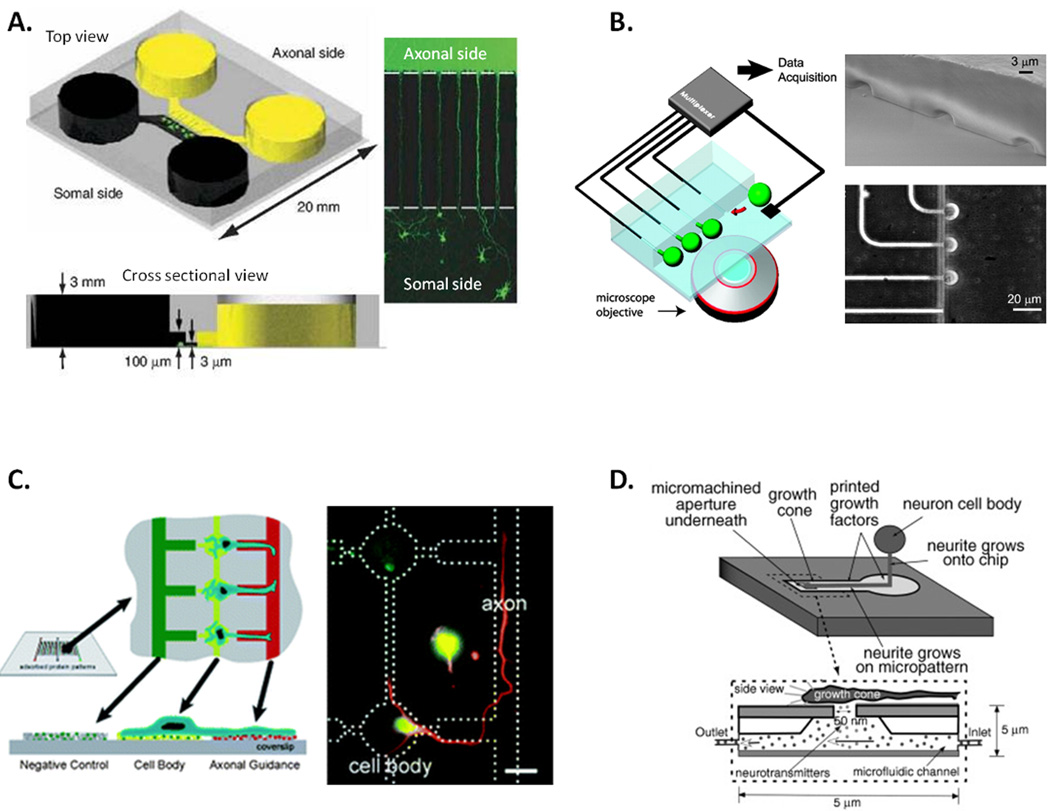
Figure 3. Systems for modeling neuronal architecture in vitro.
A) A microfluidic-based culture platform to direct axonal growth of CNS neurons; two chambers (yellow and black) are connected via sub-cellular diameter channels which allow axon growth between chambers and polarization of axonal and somal sides (Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd; Nature Methods 52 Copyright 2011). B) A microfluidic chip enabling for multiplexed electrophysiological experiments on cultured neurons: microfluidic junctions between the main cell culture chamber and lateral recording capillaries allows for patch clamp recordings of cell (green) activities (Reprinted from Ref 53 with permission from PNAS Copyright 2005 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A). C) The use of vacuum soft lithography to pattern biomolecules and direct neuronal adhesion and polarization: adhesion molecules are patterned on a glass coverslip using a microfluidic template to allow for directed cell growth (Reproduced in part from Ref 54 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry). D) the artificial synapse; a micro-aperture allows for delivery of pico liter volumes of neurotransmitter to neuronal dendrites enabling detailed investigation of synaptic activity (Reprinted from Ref 55 with permission from John Wiley and Sons Inc. Artificial Organs. Copyright 2003).