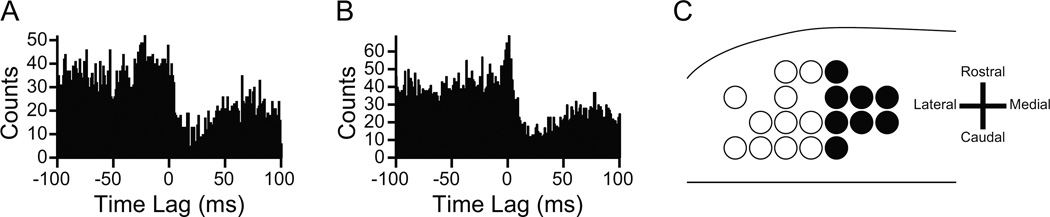
Figure 1.
(A, B) CS triggered correlograms of DCN activity that were used to identify a monosynaptic connection between the PC and DCN neuron being recorded. In (A) the correlogram shows a sharp drop in activity within a few milliseconds of the CS (t = 0). In (B) the inhibition is preceded by a brief increase in activity, presumably due to excitation of the DCN neuron by collaterals of the olivocerebellar axon. (A) and (B) are based on figure 4A, B in Blenkinsop TA and Lang EJ (2011) J Neuroscience 31: 14708–14720 with permission granted under the copyright policy of J Neuroscience. (C) Schematic of the electrode array from one experiment showing the clustering of PCs that projected to the DCN neuron being recorded. Filled circles indicate PCs that projected to the DCN neuron, open circles represent the remaining PCs in the array. The spacing between PCs was 250 µm.