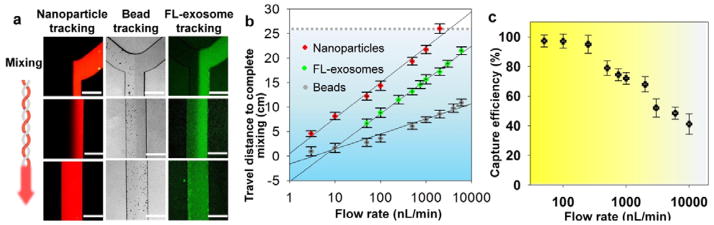
Fig. 2.
Microfluidic continuous-flow mixing for efficient exosome isolation. (a) Two-stream particle mixing in the microchannel. Left: Fluorescence CCD images of mixing process for a stream of Texas Red labeled nanoparticles (50 nm) co-flowed with a bead solution. Middle: Immuno-magnetic beads (2.8 μm) tracked under bright field for mixing with human blood plasma. Right: Mixing of fluorescently labeled exosomes with antibody beads. Exosomes were purified from ovarian cancer patient plasma by ultracentrifugation. Scale bars: 300 μm. (b) Plots of minimum travel length required for uniform mixing over a flow rate range. Grey dashed line indicates mixing channel length in the ExoSearch chip. (c) Exosome capture efficiency as a function of mixing flow rate measured using purified, fluorescently labeled exosomes and capture beads.