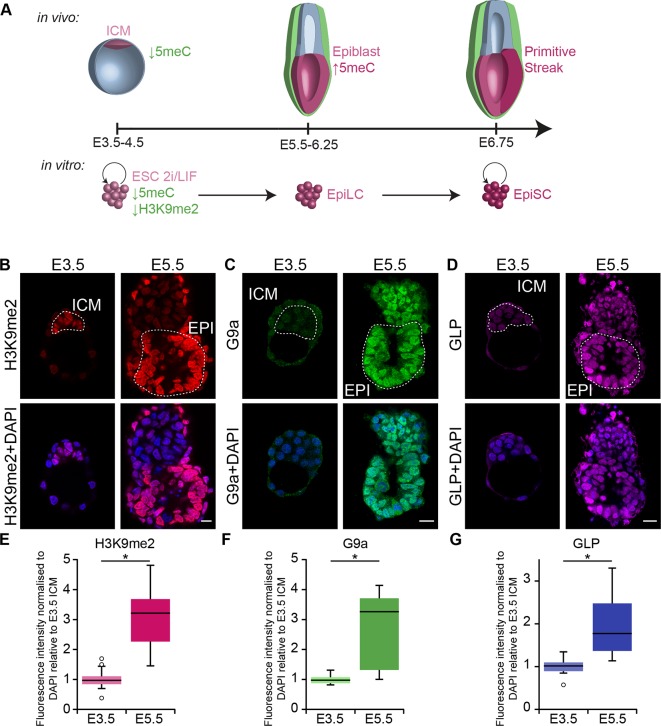
Figure 1. G9a-dependent programming occurs at implantation.
(A) Schematic of early mouse development and their in vitro equivalents. Genome-wide DNA demethylation after fertilisation leads to an epigenetic basal state with low 5meC in ICM of blastocysts. Shortly after implantation, the epiblast cells undergo epigenetic programming, which includes de novo DNA methylation. By E6.25, the epiblast is primed for somatic development, while being competent for germline specification. Gastrulation follows at E6.75. Naïve ESCs, primed EpiLCs and EpiSCs represent different stages of in vivo development. ESCs grown in 2i/LIF medium resemble the ICM, while EpiLCs, induced from ESCs after 48 h in response to FGF2 and Activin A, are equivalent to epiblast. Their prolonged culture results in EpiSCs, which are reminiscent of the anterior primitive streak (Kojima et al., 2014). (B–D) Whole-mount IF staining for H3K9me2 (B), G9a (C) and GLP (D) in E3.5 and E5.5 embryos. Dotted line shows the ICM, and the EPI. It is noteworthy that a single confocal plane is shown to maintain original IF intensity. For anti-G9a staining of E5.5 embryo, visceral endoderm was removed to reduce the background signal (scale bar = 20 μm). (E–G) Box plots showing IF signal quantification for H3K9me2 (E), G9a (F) and GLP (G). Data shows IF intensity normaliseormalized to DAPI for individual ICM or epiblast cells. At least 3 embryos and 20 cells were quantified for each time point. (*p<0.05 in Wilcoxon rank sum test). DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EPI: epiblast; EpiLCs: epiblast-like cells; ESCs: embryonic stem cells; FGF2: fibroblast growth factor 2; GLP: G9a-like protein; ICM: inner cell mass; IF: immunofluorescence; 2i/LIF: two-inhibitor/leukemia inhibitory factor.