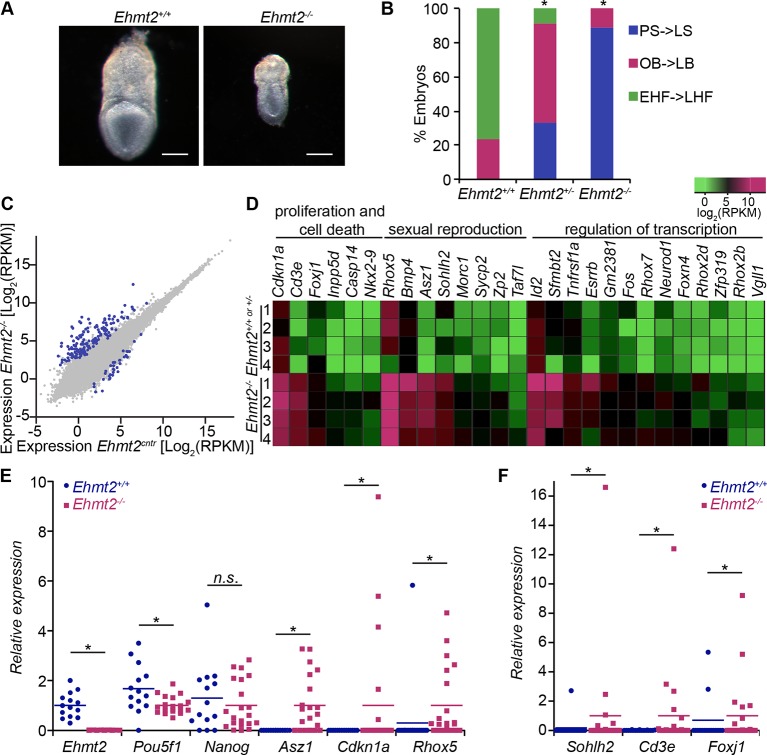
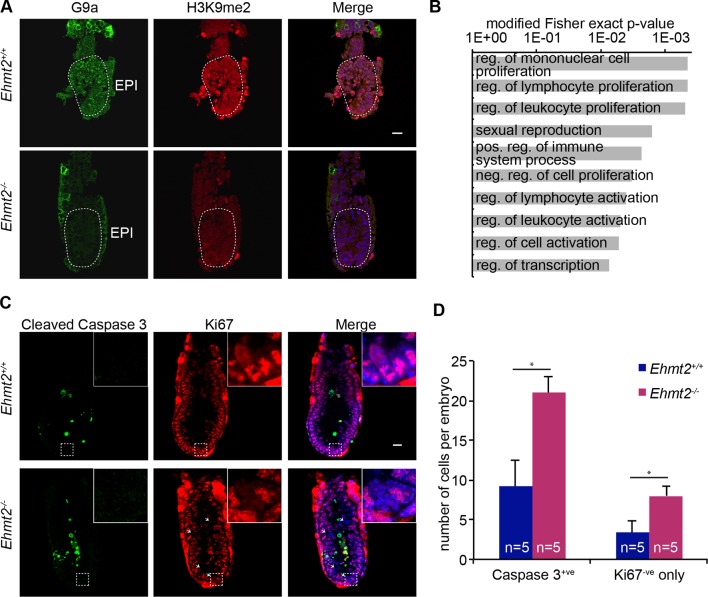
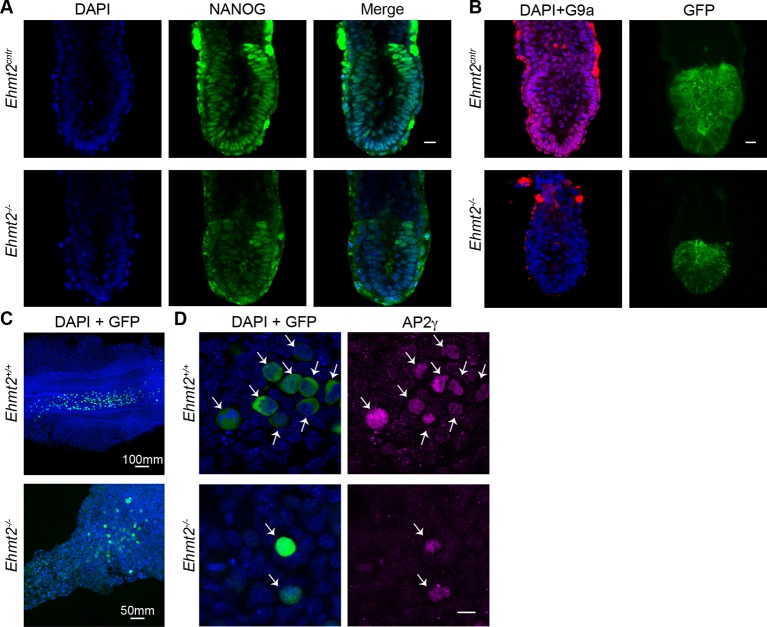
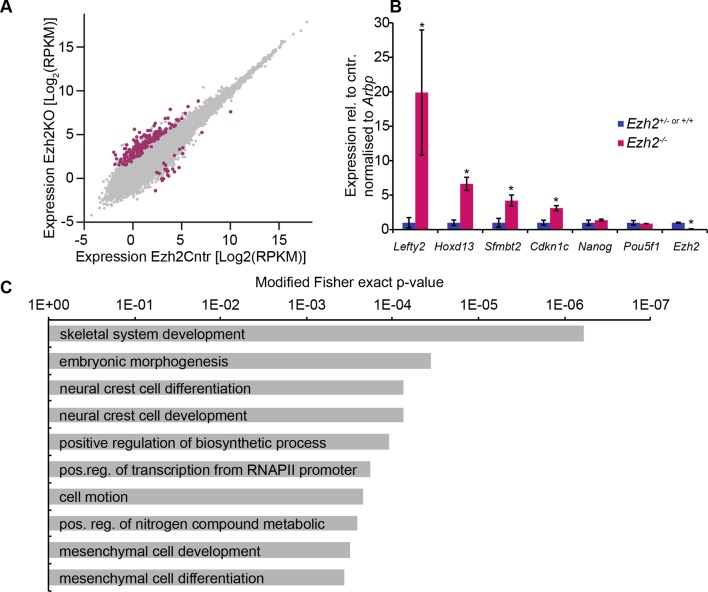
Figure 2. G9a represses germline and proliferation-related genes in the postimplantation epiblast.
(A,B) bright-field images of Ehmt2+/+and Ehmt2−/− embryos at E7.5 (A) (scale bar = 0.1 mm). At least nine embryos of each type were staged (B) (*Chi2 test p-value= <0.05). (C) Scatter plot showing transcript expression levels in Ehmt2+/+or +/−and Ehmt2−/−E6.25 epiblast. Blue points are differentially expressed genes (Log2RPKM>1, p-value<0.05, Log2(FC)>1.4). Shown is the geometric average from four biological replicates. (D) Heatmap showing expression of selected genes from enriched GO categories. (E,F) Single-cell RT-qPCR validation of RNA-seq performed on individual epiblast cells isolated from E6.25 Ehmt2+/+ or Ehmt2−/− embryos (minimum 2 embryos and 14 cells). Dot plots show levels of Ehmt2, pluripotency (Nanog, Pou5f1), germline (Asz1, Rhox5, Sohlh2) and proliferation regulators (Cdkn1a, Cd3e, Foxj1). Expression is normalised to Arbp and relative to average in Ehmt2−/− and for Ehmt2 relative to Ehmt2+/+. Statistical significance was calculated using Wilcoxon rank sum test for Pou5f1 and Nanog, where majority of WT and KO cells show detectable expression. For remaining genes a Chi2 test was used. (*p-value<0.05). Also see Figure 2—source data 1–4 and Figure 2—figure supplement 1–3. LHF: late head fold; EHF: early head fold; LB: late allantoic bud; OB: no allantoic bud; LS: late streak; PS: pre-streak. RT-qPCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; RNA-seq: RNA sequencing; WT: wild-type: KO: knockout; GO: gene ontology; FC: fold change.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09571.004