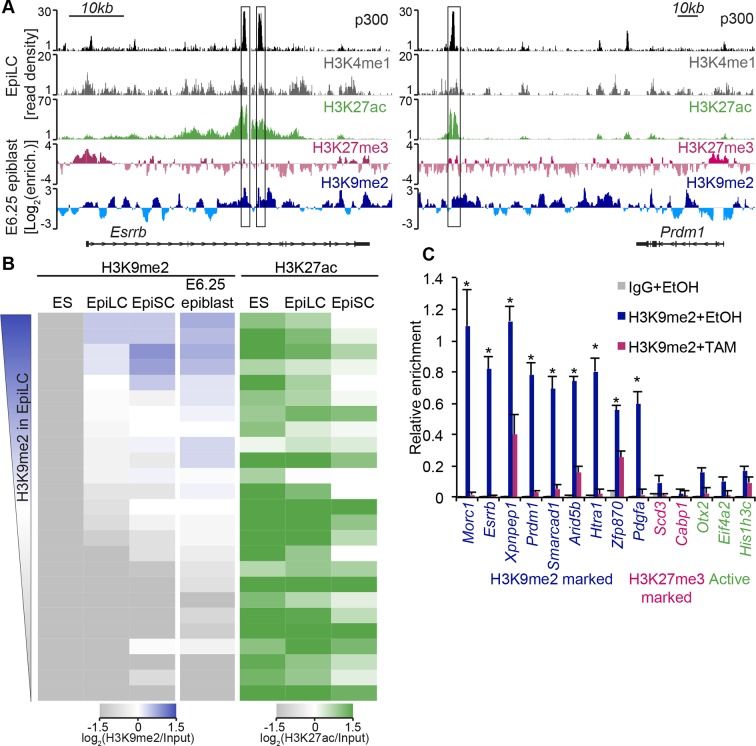
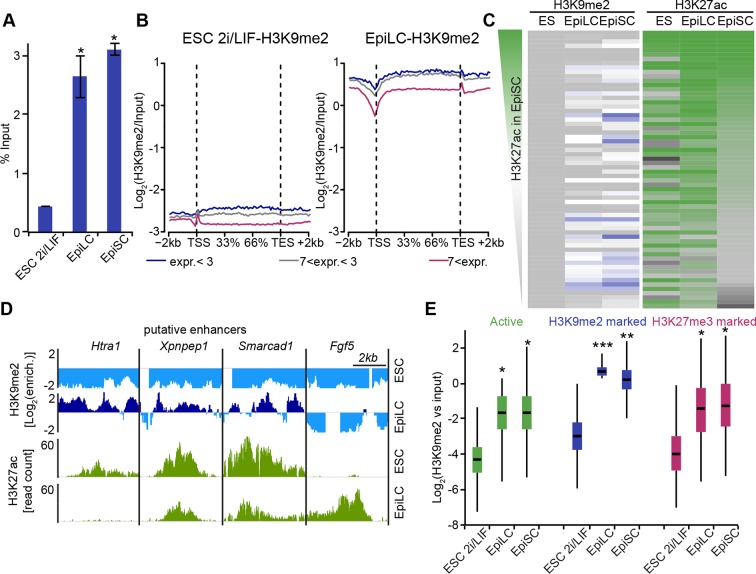
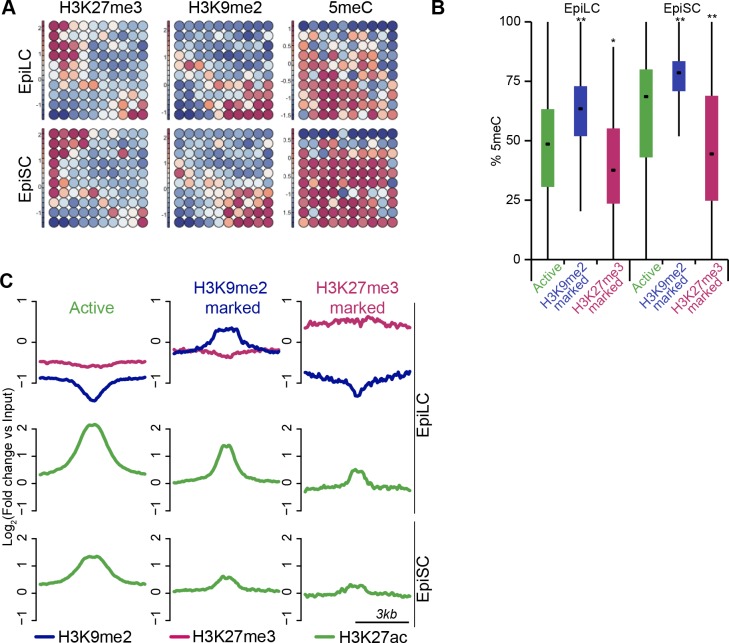
Figure 6. H3K9me2 marks enhancers undergoing inactivation during exit from naïve pluripotency.
(A) Genome browser tracks showing p300, H3K27ac, and H3K4me1 at inactive Esrrb and Prdm1 putative enhancers (black boxes) in day 2 EpiLCs (GSE56138) (Buecker et al., 2014). Bottom two tracks show H3K27me3 (red) and H3K9me2 (blue) enrichment in the E6.25 epiblast. Green and grey tracks show read density, while blue and red tracks show Log2 enrichment of ChIP sample over the input sample. (B) Heatmaps showing H3K9me2 and H3K27ac enrichment at enhancers active in ESCs grown in 2i/LIF. All ESC enhancers in 2i/LIF enriched for p300, H3K27ac and H3K4me1 were clustered using kohonen package based on H3K9me2 and H3K27ac. Individual classes were ranked based on H3K9me2 levels in EpiLCs. H3K27ac tracks were extracted from (GSE56138, GSE57409) (Buecker et al., 2014; Factor et al., 2014). (C) LcChIP-qPCR measuring H3K9me2 levels at putative enhancer elements in Ehmt2F/−CreER+ve d2 EpiLCs treated with EtOH or TAM. H3K9me2- (blue), H3K27me3- (red) marked, as well as active (green) regulatory elements are shown. Data are mean (± SD) from two independent biological replicates. (*Student’s t-test p-value<0.05 of EtOH compared with TAM treated sample). Also see Figure 6—figure supplement 1,2. H3K27ac: histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; EpiLCs: epiblast-like cells; H3K27me3: histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation; ChIP: chromatin immunoprecipitation; H3K9me2: histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation; lcChIP-seq: low cell number chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; TAM: tamoxifen; EtOH: ethanol; SD: standard deviation; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells.