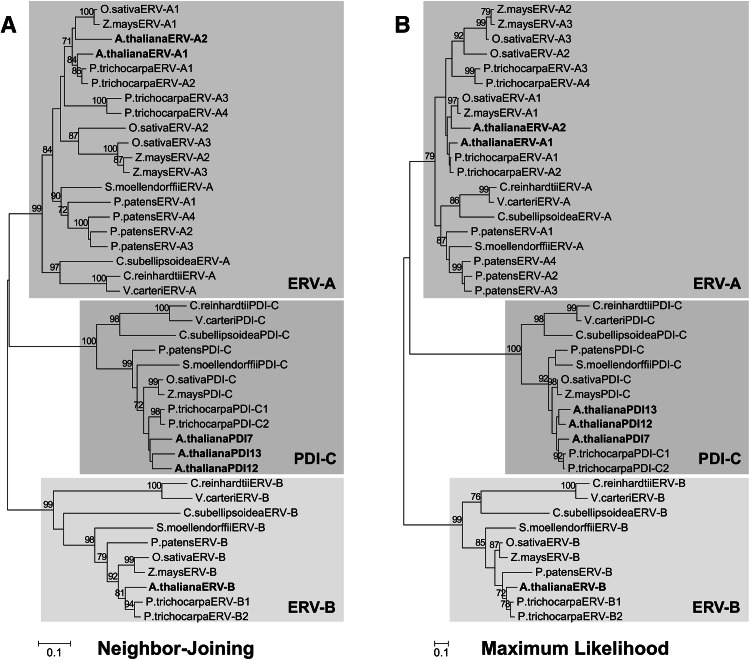
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of plant Erv41p/Erv46p homologs. a The unrooted NJ tree was generated with evolutionary distances computed using the Poisson correction method. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths proportional to the number of amino acid substitutions per site. b The unrooted ML tree was generated using the LG + G model, with 5 discrete gamma categories (+G, parameter = 0.9366). The tree with the highest log likelihood (−5049.3364) is shown, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. NJ and ML analyses were performed using a Gblocks-trimmed multiple sequence alignment consisting of 164 positions. Support values are shown above the branches, and are calculated from 1000 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values ≥70 % are shown. The three major clades are shaded, with the Arabidopsis homolog(s) in each clade highlighted in bold