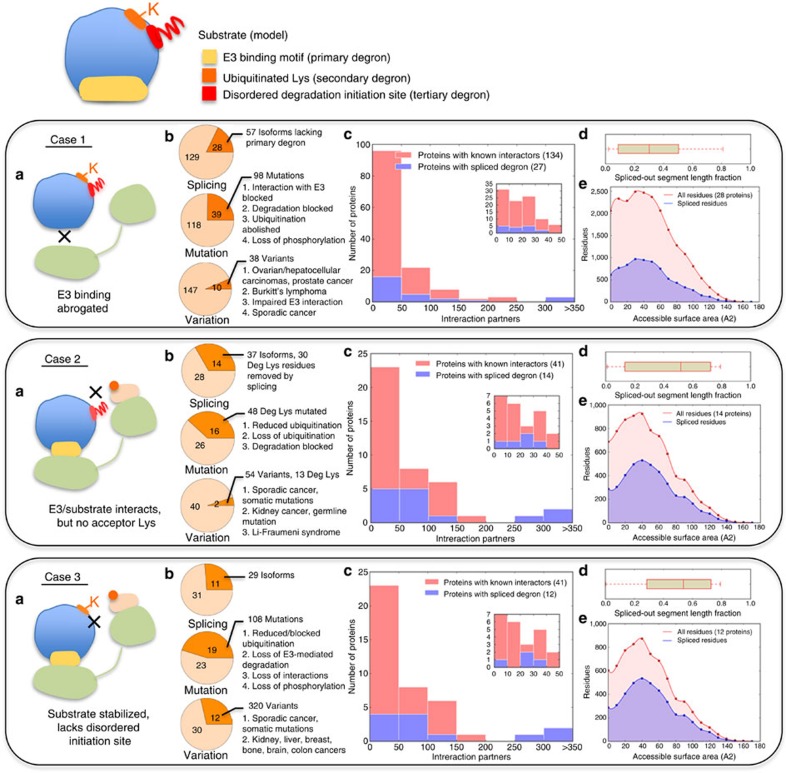
Figure 5. Tripartite degron components and functional impacts on their abrogation.
Large-scale data on alternative isoforms, mutations and sequence variations affecting the primary (case 1), secondary (case 2) and tertiary degrons (case 3). Case 1 corresponds to the 157 proteins in the primary degron data set (Supplementary Table 2), case 2 corresponds to the 42 proteins in the Deg data set (Supplementary Data 3) and case 3 refers to LDRs (predicted using IUPred) that are located nearest to the Deg lysines (that is, the tertiary degrons). For proteins in which Deg lysine(s) were located inside the tertiary degron, the mutation/variation data for the latter (case 3) include changes at the lysine(s). (a) Schematic overview of the consequences of missing (or corrupted) degrons. The same colour scheme is used as in Fig. 1. (b) Pie charts showing the number of proteins (out of the total number in each data set) for which alternative isoforms with missing degrons (top), mutations (middle) and variations (bottom) of degron components have been experimentally characterized (orange), the number of corresponding isoforms/mutants/variants and a brief description of their major functional impacts and/or associated disease outcomes (full details are provided in Supplementary Data 4–6). (c) Histograms showing the numbers of proteins that have between 0 and 50, 51 and 100, 101 and 150, and so on validated interaction partners (pink bars). Overlaid in blue are the numbers of proteins from each interaction bin that possess characterized isoforms in which degron components have been removed by alternative splicing. The insets are used to show in finer detail the bin corresponding to 0–50 interaction partners. (d) Box plot showing the length fraction (as compared with the canonical sequence) of protein segments removed by alternative splicing. (e) Plot of ASA distribution for those proteins where degron components are removed by alternate splicing. ASAs of all residues from the canonical sequence are shown in light red, whereas ASAs of residues that are removed in one or more isoforms are in blue. ASA values were predicted with SPINE-X22 using the canonical sequences as input.