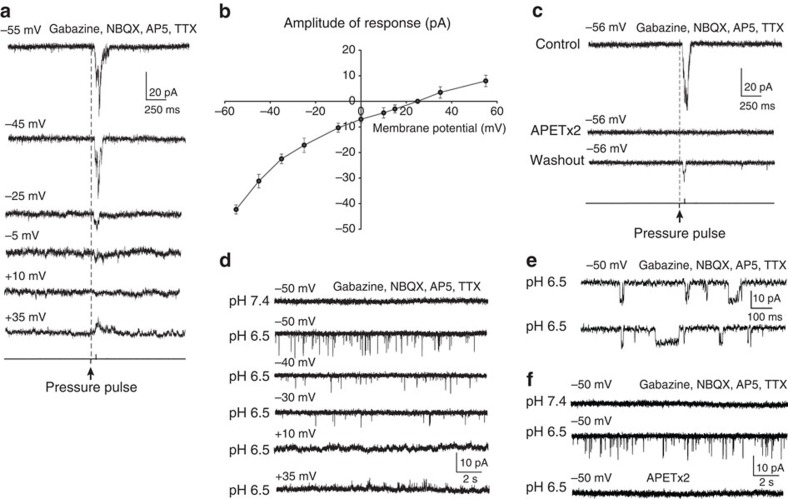
Figure 5. Voltage clamp analysis of the response to fluid pulse stimulation and to decreases in extracellular pH.
(a) The amplitude of the receptor current increases at hyperpolarised holding potentials and decreases upon depolarization in the presence of gabazine (20 μM), AP5 (100 μM), NBQX (40 μM) and TTX (1.5 μM). (b) The receptor current reversed at ∼+25 mV (n=5). (c) The receptor current evoked by fluid pulse was eliminated in the presence of the ASIC3 blocker APETx2 (1 μM) and returned after washout. The receptor currents in a–c were elicited by a fluid pulse of 60 ms, 20 p.s.i. (n=6). (d) No current events were seen at pH 7.4 in the presence of gabazine (20 μM), AP5 (100 μM), NBQX (40 μM) and TTX (1.5 μM). After a decrease in extracellular pH to 6.5, inward current deflections appeared that decreased in amplitude and frequency at more depolarized holding potentials and were reversed in sign at +35 mV (n=5). (e) At pH 6.5 discrete current deflections were recorded, which may correspond to single-channel openings. (f) The inward currents recorded at pH 6.5 were completely blocked in the presence of APETx2 (1 μM; n=3). The data in b are represented as means±s.e.m.