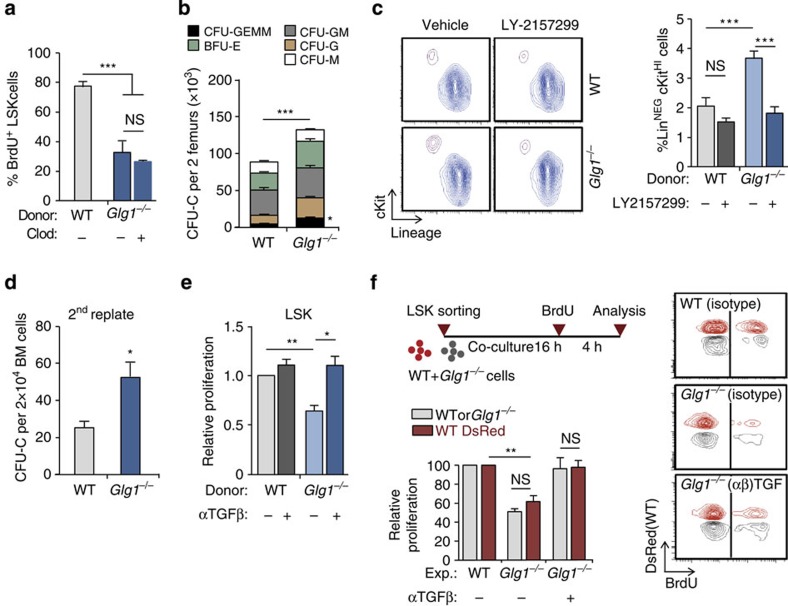
Figure 5. Haematopoietic precursors are a relevant source of TGFβ.
(a) Percentage of BrdU incorporation in WT or Glg1−/− LSK cells of control or macrophage-depleted (Clod) mice; n=5. (b) Frequency of the different types of CFU-C in mice reconstituted with WT or Glg1−/− donors; n=6. (c) Contour plots (left) and frequency (right) of LinNEG cKit+ cells obtained from WT or Glg1−/− marrow grown in the presence or absence of the TGFβRI inhibitor LY-2157299; n=6. (d) Number of secondary colonies after replating WT or Glg1−/− CFU-C from primary cultures; n=3 independent experiments. (e) Relative in vitro proliferation of WT or Glg1−/− LSK cells, as measured by BrdU incorporation; n=3 independent experiments. (f) Experimental design to test the in vitro proliferation of WT and Glg1−/− LSK cells in co-cultures with or without TGFβ blockade. Representative contour plots (right) and quantification of the relative proliferation; n=3 independent experiments. Data are shown as mean±s.e.m.; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; NS, not significant, as determined by Student's t-test (b,d), or one-way analysis of variance with Turkey's test (a,c,e and f).