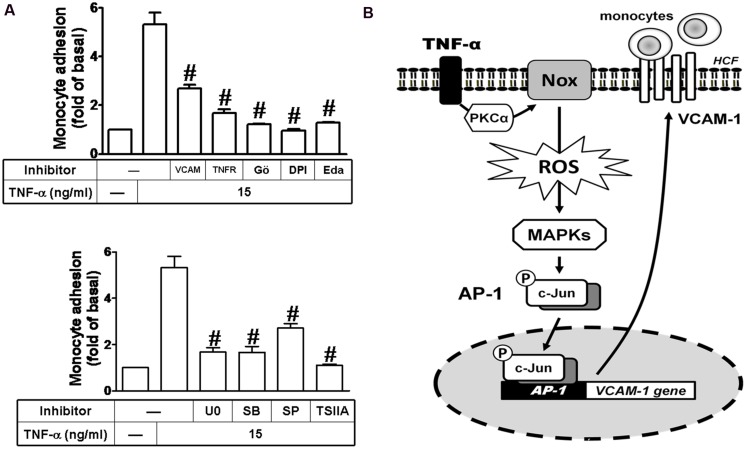
FIGURE 8.
Up-regulated VCAM-1 by TNF-α contributes to promotion of monocyte adhering to these HCFs. (A) For cell adhesion activity, cells were pretreated with VCAM-1 nAb, TNFR nAb, Gö6976 (Gö), DPI, edaravone (Eda) (Figure 7A, upper), U0126 (U0), SB202190 (SB), SP600125 (SP), or TSIIA (Figure 7A, lower) for 1 h and following by TNF-α (15 μg/ml) for 16 h prior to addition of THP-1 monocytes. The adhesion activity was determined by cell adhesion assay as described in Section “Materials and Methods”. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least five individual experiments (n = 5). #P < 0.01 as compared with TNF-α alone. (B) Schematic signaling pathways are involved in TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression in HCFs. TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression is triggered by TNF-α/TNFR-mediated signaling pathways. TNF-α-mediated responses are dependent on PKC-α-activated Nox/ROS/MAPKs cascades linking to c-Jun/AP-1 transcription activity. Up-regulation of VCAM-1 contributes to enhancement of monocyte adhering to these HCFs challenged with TNF-α. Understanding the mechanisms of VCAM-1 up-regulated by TNF-α on HCFs may provide rationally therapeutic interventions for heart injury or inflammatory diseases.