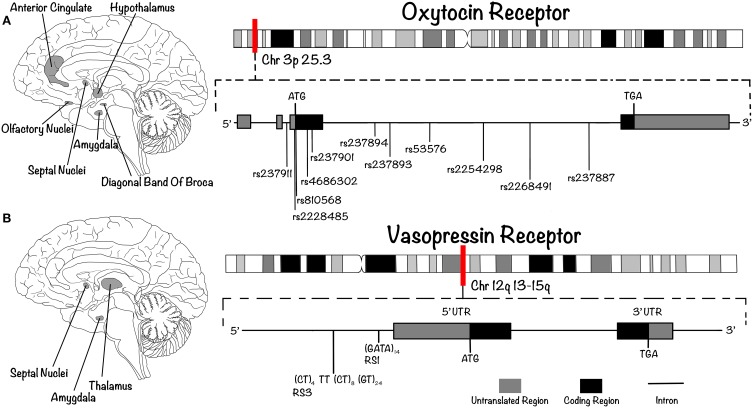
Figure 2.
OXTR and AVPR are G-protein coupled receptor expressed in key structures of the brain. Their genes present characteristic polymorphisms associated with differences in human social (and pathological) behaviors. (A) In the human brain, OXTR is expressed in the basolateral amygdala, the anterior and ventromedial hypothalamus, the olfactory nucleus, the diagonal band of Broca, the septal nuclei and the anterior cingulate (left). Its gene (right) is located on chromosome 3p25.3 (approximate position indicated by red vertical line). It contains four exons and three introns, which include several known SNPs. (B) AVPR1A is expressed in the septal nuclei, the thalamus and the basal amygdaloid nucleus (left); the gene encoding this receptor (right) is located on chromosome 12q14 (approximate position indicated by red vertical line). As in the case for OXTR, it contains an intron before the exon that encodes the seventh transmembrane domain. The schematic includes the SNPs (in the case of OXTR) and SSRs (in the case of AVPR) that are reviewed in this article.