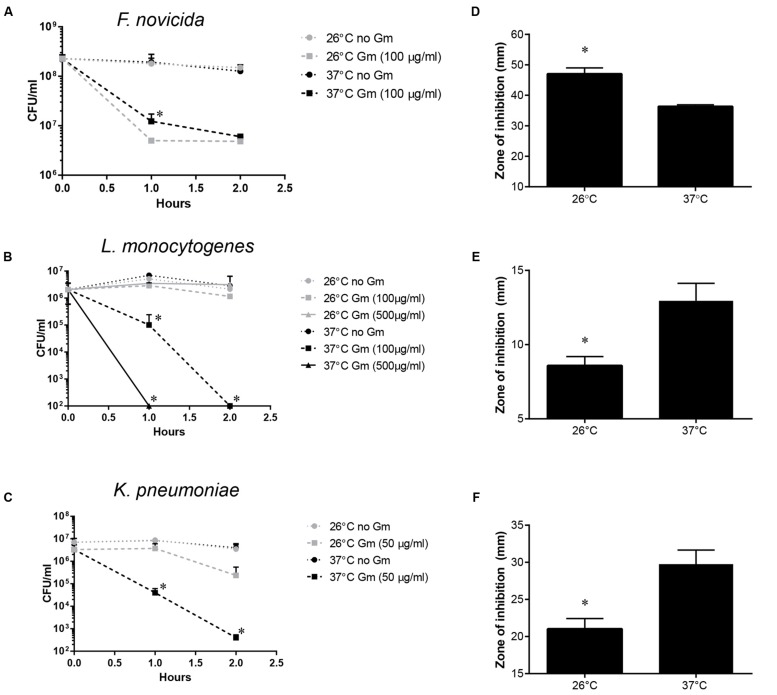
FIGURE 9.
Francisella novicida, Listeria monocytogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae exhibit temperature-dependent Gm resistance. F. novicida (A), L. monocytogenes (B), or K. pneumoniae (C) bacteria were cultivated in general growth media overnight, suspended in PBS, and treated with Gm at the indicated temperature. Bacteria were diluted and plated for viable CFU at the indicated times. Plotted values represent mean CFU ± SD. Log-transformed data were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA and a Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. ∗P < 0.05 F. novicida 26°C vs. 37°C Gm (100 μg/ml) at 1 h (A); L. monocytogenes 1 h 26°C vs. 37°C Gm (100 and 500 μg/ml), 2 h 26°C vs. 37°C Gm (100 and 500 μg/ml); K. pneumoniae 26°C vs. 37°C Gm (50 μg/ml) at 1 and 2 h. Antibiotic disk diffusion assays were carried out in which F. novicida (D), L. monocytogenes (E), or K. pneumoniae (F) bacteria were lawn streaked onto solid media, and incubated with filter disks containing the indicated amount of Gm. These plates were incubated at the temperature indicated, and zones of inhibition were measured. Bars represent the mean of the zones of inhibition ±SD. Disk diffusion data were analyzed using an unpaired t-test. ∗P = 0.0009 (D); ∗P = 0.0026 (E); ∗P = 0.0050 (F).