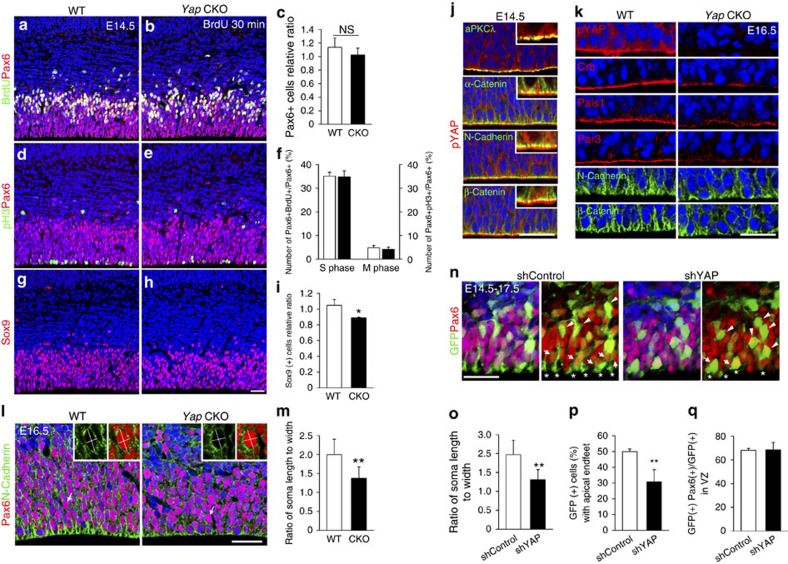
Figure 6. Yap loss causes defects in cell shape and apical attachment of cortical progenitors.
(a–f) At E14.5, the Yap CKO contains slightly fewer Pax6 (+) cells than WT, although the fractions of BrdU (+) S-phase cells and of pH3 (+) M-phase cells among total Pax6 cells are not significantly different. (g–i) Sox9 (+) cells are reduced in number in the absence of Yap. (j) In the cortical epithelium, pYap is localized in the cytoplasm and highly enriched at the apical junction; this distribution overlaps with aPKCλ and is apical to adherens junction marked by N-Cadherin, β-Catenin or α-Catenin. (k) N-Cadherin or β-Catenin labelling in apical endfeet is reduced and less concentrated in the Yap CKO than in the WT. Apical polarity complex proteins, Crb, Pals1 and Par3 are reduced at the apical surface when pYap is largely depleted at E16.5. (l,m) At E16.5, in the Yap CKO, the ratio of soma length to width of Pax6 (+) apical progenitor cells is reduced as compared with WT. (n–q) Fewer Yap KD cells have apical endfeet contacting the apical surface than control shRNA-expressing cells (arrows and *). Yap KD cells have a rounded cell shape (cellular length to width ratio is close to 1, arrow head). However, there is no difference in the proportion of Pax6 (+) cells among total GFP-expressing cells in the VZ. Two-tailed unpaired t-test reveals statistical significance (**P<0.01 and *P<0.05). Scale bars, 50 μm (a,b,d,e,g–j); 30 μm (n).