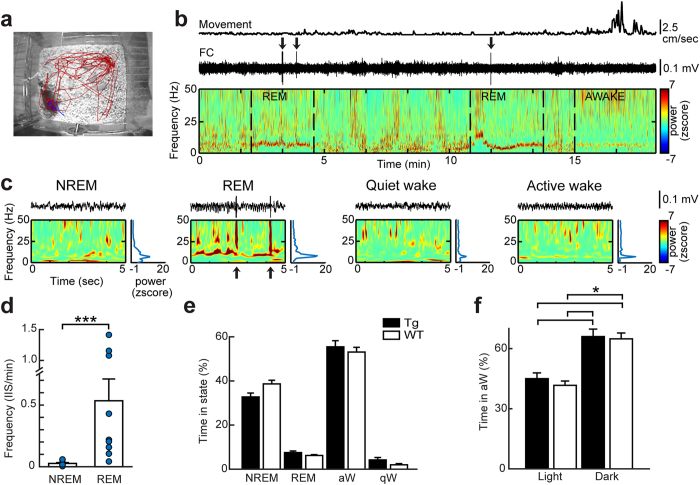
Figure 2. IIS in 5 week-old Tg2576 mice occur predominantly within REM sleep.
(a) An example of positional tracking used to monitor mouse movement in the home cage. The red line marks animal position in the previous 10 minutes while the blue line marks position in the last 60 seconds. (b) A 20 minute-long EEG recording from a 5 week-old Tg2576 mouse shows detected movement (Top), EEG (Center, frontal cortical (FC) electrode) and spectrogram (Bottom). Note that IIS (arrows) occur in the behavioral states without movement and power is high in the theta frequency band, associated with REM sleep (for definition of REM sleep and other behavioral states, see Methods). Dotted lines demarcate state transitions. (c) Representative 5 second-long EEG traces from b illustrate each behavioral state. For each behavioral state (from left to right, NREM, REM, quiet wakefulness, active wakefulness) the FC recording of the EEG is shown at the top, with the spectrogram corresponding to it shown below. To the right is the power spectrum. Note that IIS (arrows) occur in REM sleep. (d) Mean IIS frequency per minute for 24 hour-long recordings of 5 week-old Tg2576 mice. Mean IIS frequency in REM sleep epochs was greater than mean IIS frequency in NREM sleep epochs (n = 9; Mann-Whitney test, U = 47, p = 0.0002). WT mice did not exhibit IIS (n = 9 mice, Supplementary Table 1). In this figure and all others, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (e) There was no effect of genotype on the time spent in each behavioral state per 24 hour-long recording for 5 week-old Tg2576 (n = 9) and age-matched WT mice (n = 5; two-way ANOVA, F(1,55) < 0.001, p = 0.992). (f) For 5 week-old Tg2576 (n = 9) and WT mice (n = 5), there was no effect of genotype on the time spent in active wakefulness during the light or dark periods (two-way ANOVA, F(1,27)0.371, p = 0.548). However, there was a significant effect of light or dark period, with all animals spending more time in active wakefulness during the dark period (two-way ANOVA, F(1,27)36.262, p < 0.001; post-hoc test, p < 0.05).