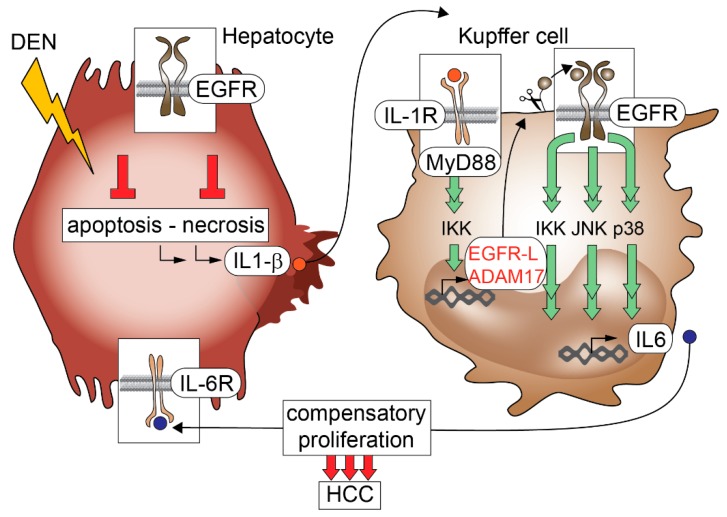
Figure 2.
EGFR function in hepatocytes and Kupffer cells during hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) formation. EGFR signaling is hepatoprotective during diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced liver damage. In the absence of EGFR, hepatocytes undergo more necrosis and apoptosis leading to increased IL-1β production, which stimulates Kupffer cells to release IL-6, which is required for compensatory proliferation and repair of damaged hepatocytes. IL-1β-induced IL-6 production in Kupffer cells is dependent on EGFR expression and occurs in a bimodal way involving the activation of the IL-1R/MyD88 pathway to first induce EGFR ligands and ADAM17 expression with subsequent EGFR transactivation required for IL-6 production via c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK, p38 and inhibitor of κB (IκB) kinase IKK. Red circles: IL-1β, Grey circles: EGFR-ligand, Blue circles: IL-6. Arrows indicate receptor activation.