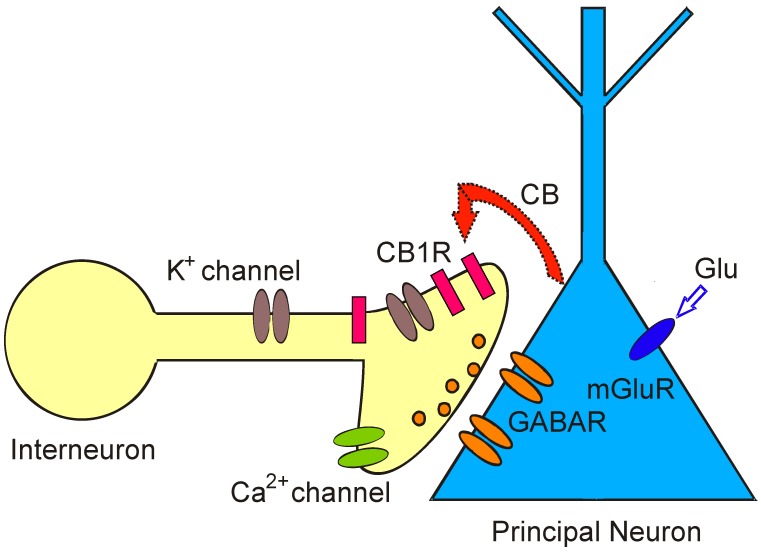
Figure 1.
Depolarization-induced Suppression of Inhibition (DSI) is a model for retrograde signaling in the brain and allows assaying real time release of endoCBs from principal neurons as a brief cessation of GABA ouput. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) by glutamate (Glu) on principal neurons or depolarization of postsynaptic principal cells evokes synthesis and release of cannabinoids (CB). Cannabinoids bind to presynaptic cannabinoid receptors (CB1R) on GABAergic interneurons and transiently reduce GABA release from synaptic terminals. As a consequence, GABAA receptor-mediated synaptic currents and GABAergic inhibition are temporarily suppressed in postsynaptic principal neurons.