Fig. 8.
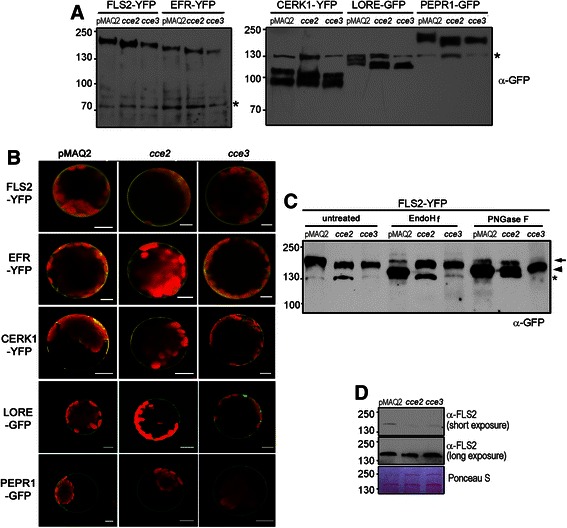
Glycosylation and localization of PRRs in the cce2/cce3 mutants. a Plasmid constructs for expressing p35S::PRR-YFP/GFP fusions were transfected into protoplasts isolated from the indicated genotypes and analyzed by western blotting with an α-GFP antibody. The asterisks mark unspecific bands recognized by the GFP antibody, which was used as an internal loading control. Note that different buffers (see methods section) were used for protein extraction in the right or left panels. Numbers on the left are the molecular size markers in kDa. b Confocal microscopical images of the GFP- or YFP- tagged PRRs in the pMAQ2 parental, cce2 or cce3 background. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transiently transfected with plasmids for expressing the indicated PRRs. Scale bars represent 10 μm. c FLS2-GFP was expressed in protoplasts as described above in A, and extracted membrane proteins were subjected to endoglycosidase H (EndoHf) or peptide:N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) digestion. An arrow marks the weak glycosidase-resistant FLS-YFP bands while the arrowhead marks the mobility shift of the digested proteins. In the cce mutants, Endo Hf-resistance results from altered N-glycan structure upon blockage of the ALG3 step in the pathway (see Additional file 1: Figure S1). In the PNGase-F digests, remaining weak bands of FLS2-YFP in both wildtype (pMAQ2) and cce lanes may be explained by about 10 % core fucose-decorated (and thus PNGase F-resistant) N-glycans with terminal GlcNAc residues (see Table II of Kajiura et al. [44]), indicative of passage through the Golgi apparatus after correct folding of FLS2-YFP in the ER. Note that the ~130 kDa bands (marked with asterisk) are unspecific signals that appear with the anti-GFP antibody. d Endogenous FLS2 levels in the cce2/cce3 mutants were compared to the pMAQ2 parental line. Western blotting (α-FLS2) was used to visualize FLS2 levels in microsomal proteins prepared from 8-day-old seedlings
