Figure 2.
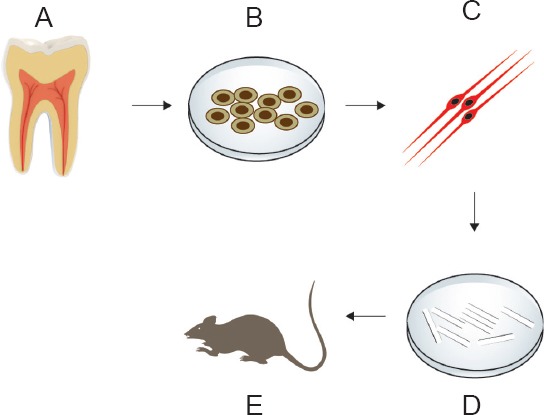
Dental pulp stem cell (DPSC)-derived SCs in peripheral nerve injury regeneration.
Dental pulp is extracted from healthy adult human teeth (A). DPSCs are cultured in a special serum-free medium to ensure that the resulting stem cells are of neural crest ontogeny (B). Nerual crest-derived DPSCs are induced to differentiate into Schwann cells, which is characterized by Schwann cell marker expression and neurotrophic factor secretion (C). Schwann cells are seeded on scaffolds in vitro to study their ability to survive and multiply in a 3D structure (D). Schwann cells seeded on a suitable scaffold are transplanted into an in vivo PNS injury model (e.g., rat sciatic nerve injury) and healing is monitored according to specific criteria (E).
