Figure 1.
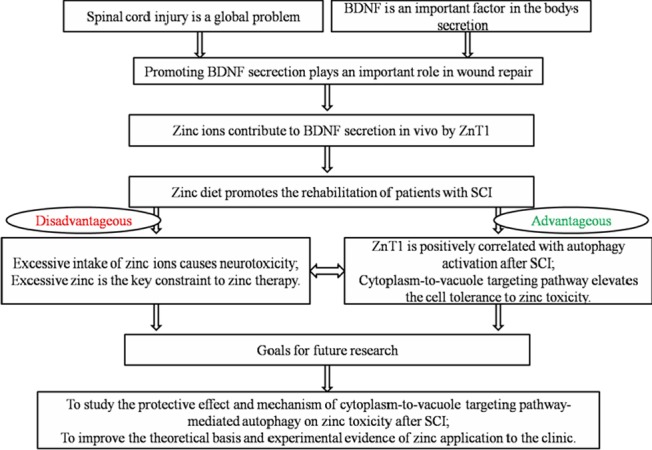
Effects and mechanism of zine on the recovery of neurological function after SCI.
In our previous studies, we have found that zinc ions could improve the expression of BDNF in the spinal cord tissues after SCI. Unfortunately, excessive zinc ions would cause neurotoxicity in spinal cord tissues and the excessive zinc is the key constraint to the zinc therapy after SCI. Besides, we have verified the positive correlation of ZnT1 with autophagy activation after SCI. Furthermore, some reports have claimed that the cytoplasm-to-vacuole targeting pathway could elevate the cell tolerance to the zinc toxicity. Therefore, the goals for the further research as follows: Studying the protective effect and mechanism of cytoplasm-to-vacuole targeting pathway-mediated autophagy on zinc toxicity after SCI, which may improve the theoretical basis and experimental evidence of zinc application to the clinic treatment for SCI. BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; SCI: spinal cord injury.
