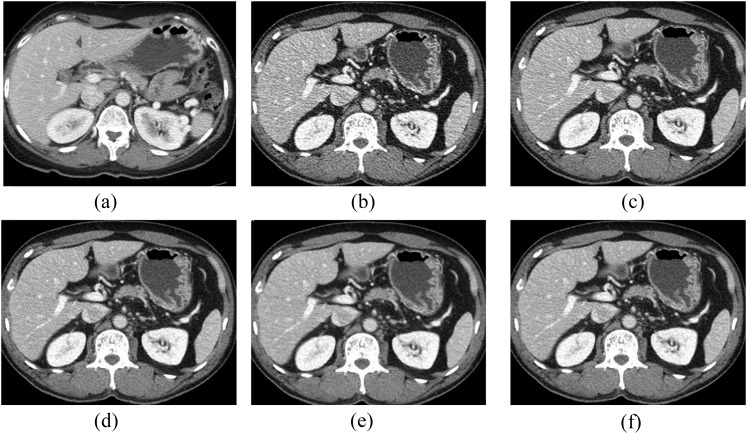
Figure 1.
Transverse abdominal CT images in a 50-year-old female with a body mass index of 23.53 kg m−2. Lower dose CT reconstruction included filtered back projection (b), adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) 40% (c), ASIR-V 30% (d), ASIR-V 50% (e) and ASIR-V 70% (f). The volume CT dose index for lower dose series was 4.7 mGy, representing 44% dose reduction relative to routine-dose ASIR 40% series (a). At the same reduced radiation dose CT series, all ASIR-V (d–f) images are less noisy without affecting the diagnostic acceptability. Compared with routine dose 40% ASIR series (a), both readers considered that, among the reduced radiation dose CT series, 50% ASIR-V series are nearly identical in image noise, sharpness and diagnostic acceptability without artefacts (e). The readers interpreted 70% ASIR-V series showing slightly blocky pixilated appearance at the tissue interfaces.